In hospitalized patients with acute kidney injury, a BUN/creatinine ratio less than or equal to 12 suggests the diagnosis of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, finds a study published in BMCNephrol
An experienced nephrologist performed all of the kidney biopsies. Prior to the procedure, all the patients were normotensive, and kidney size and anatomy were evaluated via ultrasound. Following the localization of the left kidney inferior pole, the puncture site was marked, the skin was prepared with chlorhexidine, and 1% lidocaine was used for local anesthesia.
Histologically, AIN was defined as interstitial edema and interstitial infiltrate consisting primarily of mononuclear or polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Tubulitis was defined as the invasion of the tubular basement membrane by inflammatory cells [In accordance with their respective distributions, continuous variables were expressed by the mean ± standard deviation or the median with interquartile range. The normality of the distribution was evaluated by using the Kolmogorov‒Smirnov test.
The optimal BCR value for discriminating AIN was identified by using a ROC analysis. The Youden point was selected to maximize the sensitivity over the specificity. The bilateral p-value for statistical significance was established at < 0.05. The statistical analysis was performed by using R in the R-Studio.Five hundred thirty patients diagnosed with AKI were assessed, of whom 42 patients satisfied the inclusion criteria and underwent a percutaneous renal biopsy (Fig.
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 I'm happy that Diablo 4 is just a prettier Diablo 3Diablo 4's release can't come soon enough.
I'm happy that Diablo 4 is just a prettier Diablo 3Diablo 4's release can't come soon enough.
Weiterlesen »
 Associations between severe and notifiable respiratory infections during the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital anomalies at birth: a register-based cohort study - BMC Pregnancy and ChildbirthBackground Evidence regarding the association between acute respiratory infections during pregnancy and congenital anomalies in babies, is limited and conflicting. The aim of this study was to examine the association between acute respiratory infections during the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital anomalies in babies using record linkage. Methods We linked a perinatal register to hospitalisation and disease notifications in the Australian state of New South Wales (NSW) between 2001 to 2016. We quantified the risk of congenital anomalies, identified from the babies’ linked hospital record in relation to notifiable respiratory and other infections during pregnancy using generalized Estimating Equations (GEE) adjusted for maternal sociodemographic and other characteristics. Results Of 1,453,037 birth records identified from the perinatal register between 2001 and 2016, 11,710 (0.81%) mothers were hospitalised for acute respiratory infection, 2850 (0.20%) had influenza and 1011 (0.07%) had high risk infections (a record of cytomegalovirus, rubella, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, chickenpox (varicella) and zika) during the pregnancy. During the first trimester, acute respiratory infection, influenza and high-risk infections were reported by 1547 (0.11%), 399 (0.03%) and 129 (0.01%) mothers. There were 15,644 (1.08%) babies reported with major congenital anomalies, 2242 (0.15%) with cleft lip/ plate, 7770 (0.53%) with all major cardiovascular anomalies and 1746 (0.12%) with selected major cardiovascular anomalies. The rate of selected major cardiovascular anomalies was significantly higher if the mother had an acute respiratory infection during the first trimester of pregnancy (AOR 3.64, 95% CI 1.73 to 7.66). The rates of all major congenital anomalies and all major cardiovascular anomalies were also higher if the mother had an acute respiratory infection during the first trimester of pregnancy, however the difference was no statisticall
Associations between severe and notifiable respiratory infections during the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital anomalies at birth: a register-based cohort study - BMC Pregnancy and ChildbirthBackground Evidence regarding the association between acute respiratory infections during pregnancy and congenital anomalies in babies, is limited and conflicting. The aim of this study was to examine the association between acute respiratory infections during the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital anomalies in babies using record linkage. Methods We linked a perinatal register to hospitalisation and disease notifications in the Australian state of New South Wales (NSW) between 2001 to 2016. We quantified the risk of congenital anomalies, identified from the babies’ linked hospital record in relation to notifiable respiratory and other infections during pregnancy using generalized Estimating Equations (GEE) adjusted for maternal sociodemographic and other characteristics. Results Of 1,453,037 birth records identified from the perinatal register between 2001 and 2016, 11,710 (0.81%) mothers were hospitalised for acute respiratory infection, 2850 (0.20%) had influenza and 1011 (0.07%) had high risk infections (a record of cytomegalovirus, rubella, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, chickenpox (varicella) and zika) during the pregnancy. During the first trimester, acute respiratory infection, influenza and high-risk infections were reported by 1547 (0.11%), 399 (0.03%) and 129 (0.01%) mothers. There were 15,644 (1.08%) babies reported with major congenital anomalies, 2242 (0.15%) with cleft lip/ plate, 7770 (0.53%) with all major cardiovascular anomalies and 1746 (0.12%) with selected major cardiovascular anomalies. The rate of selected major cardiovascular anomalies was significantly higher if the mother had an acute respiratory infection during the first trimester of pregnancy (AOR 3.64, 95% CI 1.73 to 7.66). The rates of all major congenital anomalies and all major cardiovascular anomalies were also higher if the mother had an acute respiratory infection during the first trimester of pregnancy, however the difference was no statisticall
Weiterlesen »
 Engineering donor lymphocytes with Fas ligand protein effectively prevents acute graft-versus-host diseaseKey Points. Donor T cells engineered to display on their surface SA-FasL protein undergo apoptosis following activation by host alloantigensSA-FasL on donor lym
Engineering donor lymphocytes with Fas ligand protein effectively prevents acute graft-versus-host diseaseKey Points. Donor T cells engineered to display on their surface SA-FasL protein undergo apoptosis following activation by host alloantigensSA-FasL on donor lym
Weiterlesen »
 Smelling other people's sweat could reduce social anxiety, suggests studyApparently, smelling other people’s body odour could provide a calming effect that helps with social anxiety.
Smelling other people's sweat could reduce social anxiety, suggests studyApparently, smelling other people’s body odour could provide a calming effect that helps with social anxiety.
Weiterlesen »
 New study suggests broad neutralizing antibody could provide three years of COVID protectionIn a recent article published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, researchers showed that a novel, lab-engineered monoclonal antibody (mAb), adintrevimab conferred up to 50% protection against symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, it demonstrated this exceptional efficacy in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–naïve individuals even at titers as low as 1:30.
New study suggests broad neutralizing antibody could provide three years of COVID protectionIn a recent article published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, researchers showed that a novel, lab-engineered monoclonal antibody (mAb), adintrevimab conferred up to 50% protection against symptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, it demonstrated this exceptional efficacy in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–naïve individuals even at titers as low as 1:30.
Weiterlesen »
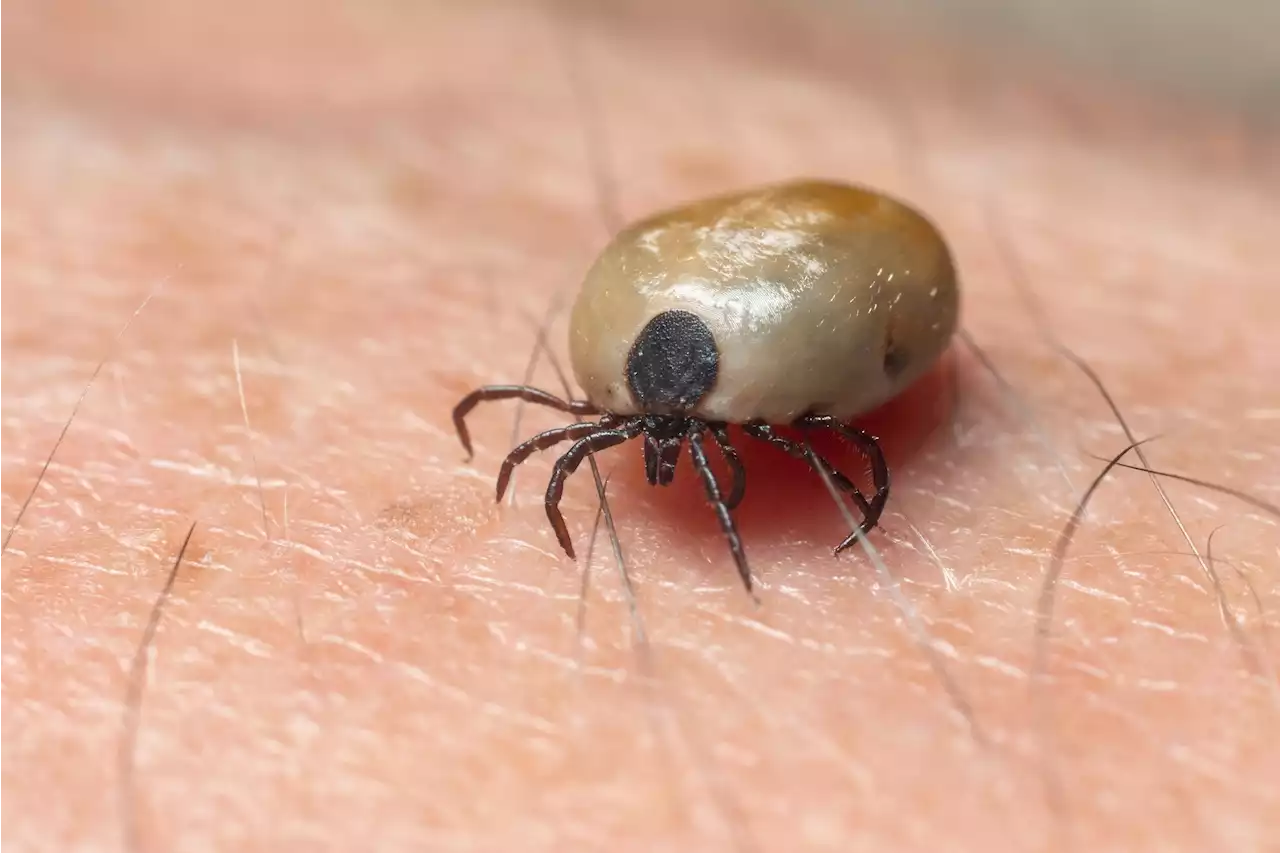 Study details bacterial agents in 418 ticks extracted from humans in FranceIn a recent study published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, researchers analyzed ticks that bit humans between January 2014 and March 2021 in France for the presence of bacterial pathogens.
Study details bacterial agents in 418 ticks extracted from humans in FranceIn a recent study published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, researchers analyzed ticks that bit humans between January 2014 and March 2021 in France for the presence of bacterial pathogens.
Weiterlesen »
