A study examining 1031 hospitalized COVID-19 patients found that aging significantly impacts immune responses, viral dynamics, and the nasal microbiome, with older adults experiencing more severe disease symptoms and delayed viral clearance.
By Vijay Kumar MalesuApr 18 2024Reviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc. In a recent study published in the journal Science Translational Medicine , researchers investigated the impact of aging on immune response, viral dynamics, and nasal microbiome in 1031 hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients, using advanced profiling techniques to understand age-related differences in disease severity and immune function.
Background Age is a significant risk factor for severe COVID-19 outcomes, with older adults facing drastically higher risks of complications and mortality than younger individuals. Despite high vaccination rates, older adults are still profoundly vulnerable. Aging correlates with elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, like interleukin-6 , which are critical markers of COVID-19 severity, hinting at a link between aging and disease pathophysiology.
Statistical analysis was performed using R software. Initial assessments were done within 72 hours of hospital admission, followed by longitudinal evaluations at subsequent visits. Data analysis applied various statistical methods depending on the data type and required adjustments for factors like age, sex, and baseline disease severity.
Related StoriesAt the initial hospital visit, typically within 72 hours of admission, a range of diagnostic assays was conducted. These included transcriptional profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and nasal swabs, serum inflammatory protein profiling, whole blood mass cytometry , nasal metatranscriptomics, and SARS-CoV-2 antibody assays.
Covid-19 Immune Response Virus Antibody Blood Cell Coronavirus Cytokines Gene Hospital Interferon Interleukin Interleukin-6 Medicine Microbiome Monocyte Mortality Pathophysiology Respiratory SARS SARS-Cov-2
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Geraniol alleviates cognitive decline in D-galactose-induced aging miceA new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as 'Aging (Albany NY)' and 'Aging-US' by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 6, entitled, 'Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation-mediated cognitive impairment in D galactose-induced mouse aging model.
Geraniol alleviates cognitive decline in D-galactose-induced aging miceA new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as 'Aging (Albany NY)' and 'Aging-US' by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 6, entitled, 'Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation-mediated cognitive impairment in D galactose-induced mouse aging model.
Weiterlesen »
 Aging reduces the ability of regulatory T cells to enhance myelin regeneration, study findsRegulatory T lymphocytes are cells that are responsible for regulating the immune system and have regenerative functions in many contexts, including myelin restoration.
Aging reduces the ability of regulatory T cells to enhance myelin regeneration, study findsRegulatory T lymphocytes are cells that are responsible for regulating the immune system and have regenerative functions in many contexts, including myelin restoration.
Weiterlesen »
 Our cells are less likely to express longer genes as we age, researchers sayAging may be less about specific 'aging genes' and more about how long a gene is. Many of the changes associated with aging could be occurring due to decreased expression of long genes, say researchers in an opinion piece published March 21 in the journal Trends in Genetics.
Our cells are less likely to express longer genes as we age, researchers sayAging may be less about specific 'aging genes' and more about how long a gene is. Many of the changes associated with aging could be occurring due to decreased expression of long genes, say researchers in an opinion piece published March 21 in the journal Trends in Genetics.
Weiterlesen »
 Texans are aging: Is the state ready to battle Alzheimer's disease?Nearly 12% of Texas seniors in 2020 were living with Alzheimer's disease.
Texans are aging: Is the state ready to battle Alzheimer's disease?Nearly 12% of Texas seniors in 2020 were living with Alzheimer's disease.
Weiterlesen »
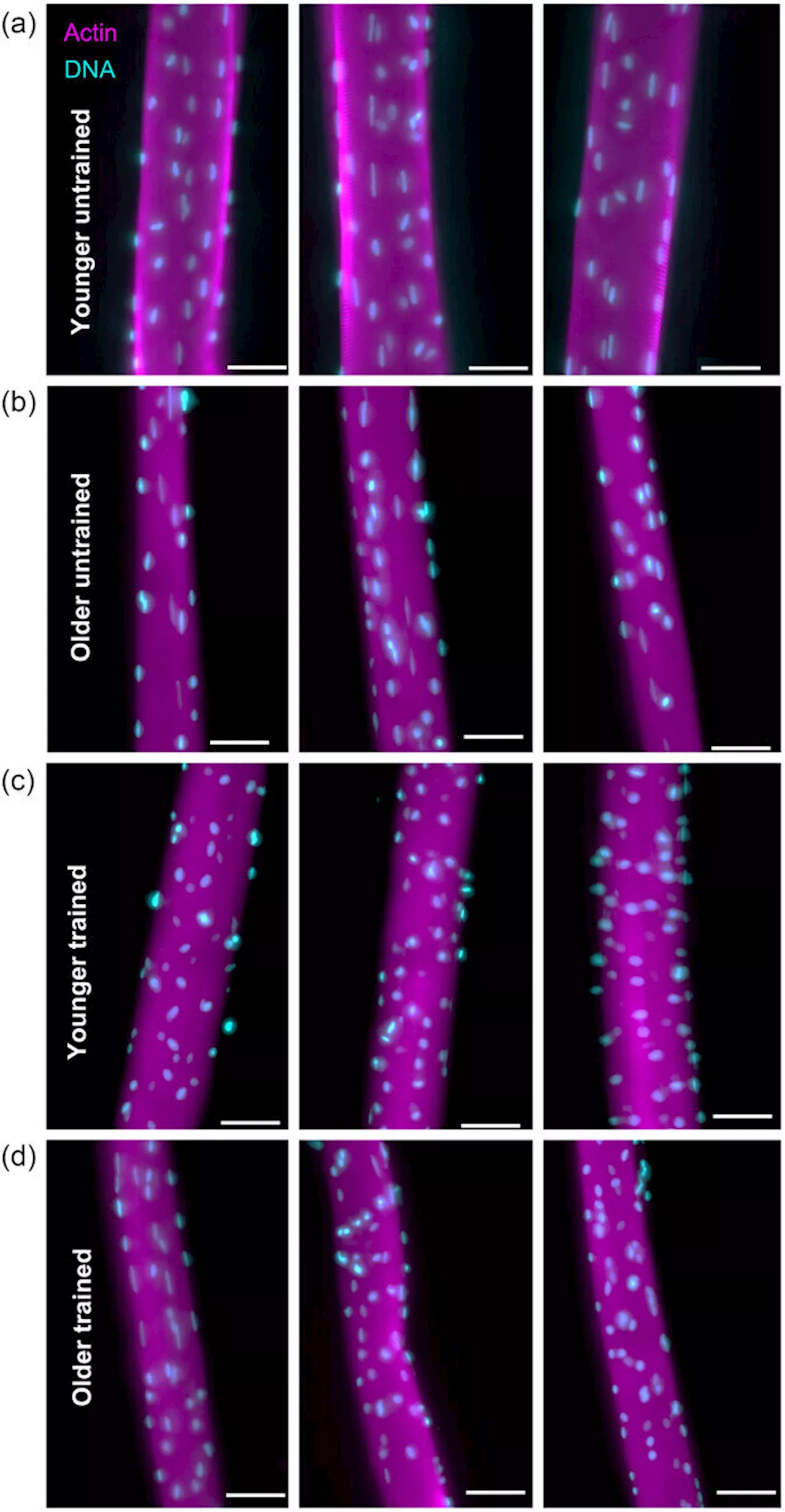 Muscle health may be informed by activity level rather than aging processA new study comparing muscle structure between active and inactive people has found that older people who regularly do endurance exercise maintain similar muscle characteristics to younger counterparts.
Muscle health may be informed by activity level rather than aging processA new study comparing muscle structure between active and inactive people has found that older people who regularly do endurance exercise maintain similar muscle characteristics to younger counterparts.
Weiterlesen »
 Social isolation may accelerate biological aging and raise mortality riskA new study from Mayo Clinic finds that socially isolated people are more likely to show signs of being biologically older than their age and more likely to die from a variety of causes.
Social isolation may accelerate biological aging and raise mortality riskA new study from Mayo Clinic finds that socially isolated people are more likely to show signs of being biologically older than their age and more likely to die from a variety of causes.
Weiterlesen »