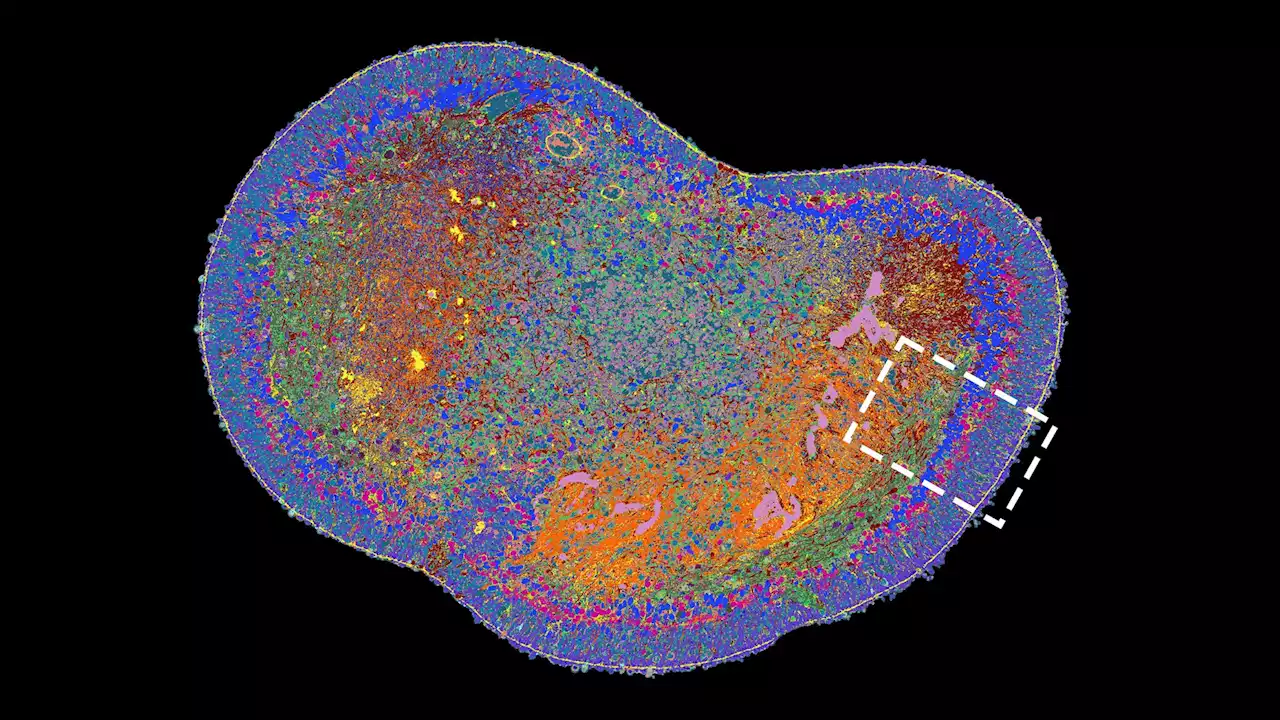
Researchers have developed a new imaging technique using organoids to map the development of human tissues and understand diseases.
A specialized atlas that will address issues like which cell types are located in which areas of human tissue as well as which genes and proteins are active in specific cells is currently under development. This atlas is anticipated to map not only tissue that has been directly separated from individuals but also organoids, which are small-scale, three-dimensional collections of tissue that are grown in the lab.
Together with Barbara Treutlein, Professor of Quantitative Developmental Biology at ETH Zurich in Basel, researchers from the Universities of Zurich and Basel have created a novel method to collect and compile a wealth of data on organoids and their development in order to contribute to the creation of such an atlas.The human retina organoids that the researchers created from stem cells were the subject of their method.
In contrast, the 3 dyes employed in 4i technology are removed from the tissue sample after measurements have been made, and 3 new proteins are stained in their place. Acarried out this task 18 times in total over the course of 18 days. Finally, a computer combines all of the individual photos into a single microscope image that shows 53 distinct proteins. These proteins offer details on the operation of the many retinal cell types, including the rods, cones, and ganglion cells.
The goal of the study is to determine when this process starts and how to halt it. In order to construct an atlas that details the growth of human organoids and tissues, Treutlein and her colleagues are now working on adapting the new precise mapping approach to additional tissue types, such as various tumor tissues and various parts of the human brain.
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Straightening Out AI: How MIT Researchers Bridge the Gap Between Human and Machine VisionResearchers identify a property that helps computer vision models learn to represent the visual world in a more stable, predictable way. MIT researchers found that adversarial training improves perceptual straightness in computer vision models, making them more similar to human visual processing
Straightening Out AI: How MIT Researchers Bridge the Gap Between Human and Machine VisionResearchers identify a property that helps computer vision models learn to represent the visual world in a more stable, predictable way. MIT researchers found that adversarial training improves perceptual straightness in computer vision models, making them more similar to human visual processing
Weiterlesen »
 Researchers Seek to Understand Post-COVID Autoimmune RiskThree large studies link past SARS-CoV-2 infection to new-onset autoimmune disease, but it is not yet clear what drives this relationship.
Researchers Seek to Understand Post-COVID Autoimmune RiskThree large studies link past SARS-CoV-2 infection to new-onset autoimmune disease, but it is not yet clear what drives this relationship.
Weiterlesen »
 AI Researchers Worry the U.S. and China Will Leave Everyone Else BehindAfter ChatGPT sparked a frenzy among tech companies, a conference in Africa is focusing on AI’s promise and peril for poorer nations.
AI Researchers Worry the U.S. and China Will Leave Everyone Else BehindAfter ChatGPT sparked a frenzy among tech companies, a conference in Africa is focusing on AI’s promise and peril for poorer nations.
Weiterlesen »
![]() Time tracking for early-career researchers: a practical guideTime management isn’t taught at graduate school, but a better understanding of how you pass the hours can help you achieve your goals.
Time tracking for early-career researchers: a practical guideTime management isn’t taught at graduate school, but a better understanding of how you pass the hours can help you achieve your goals.
Weiterlesen »
 Indigenous missing person cases get researchers' attentionA New Mexico task force charged with addressing missing person cases involving Native Americans is teaming up with researchers in Nebraska on a data collection project.
Indigenous missing person cases get researchers' attentionA New Mexico task force charged with addressing missing person cases involving Native Americans is teaming up with researchers in Nebraska on a data collection project.
Weiterlesen »
 Indigenous missing person cases get researchers' attentionA New Mexico task force charged with addressing missing person cases involving Native Americans is teaming up with researchers in Nebraska on a data collection project
Indigenous missing person cases get researchers' attentionA New Mexico task force charged with addressing missing person cases involving Native Americans is teaming up with researchers in Nebraska on a data collection project
Weiterlesen »