Juice concentrate from Japanese fruit benefits cardiovascular health, scientists report TempleUniv
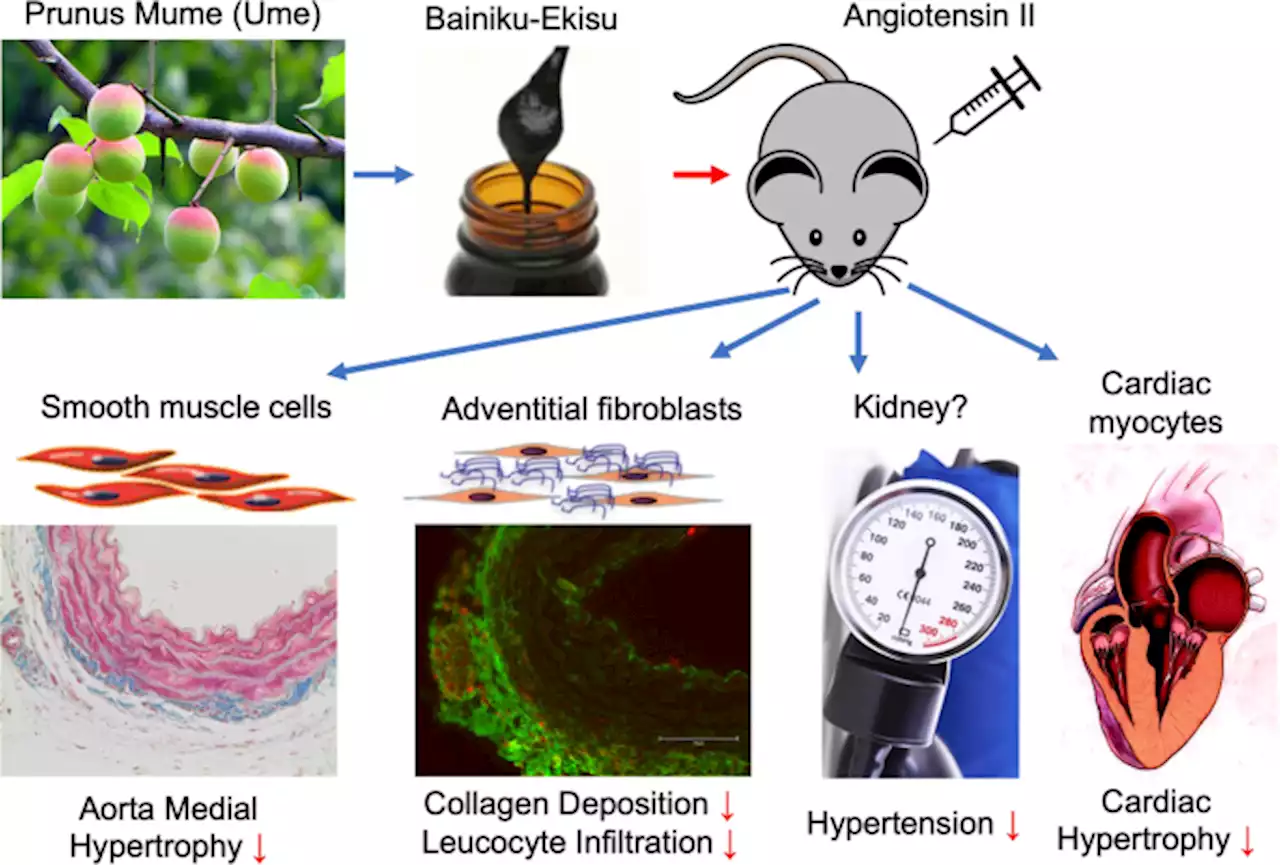
tree is a traditional food in Japan. Recently, bainiku-ekisu, an infused juice concentrate of Japanese, is attracting attention as a health promoting supplement. Angiotensin II plays a central role in development of hypertension. It has been reported that bainiku-ekisu treatment attenuates the growth-promoting signaling induced by Ang II in vascular smooth muscle cells. However, whether bainiku-ekisu has any effect on an animal model of hypertension remains unknown.
After 2 weeks, mice were euthanized, and the aortas were collected for evaluation of remodeling. Aortic medial hypertrophy was observed in control mice after Ang II infusion, which was attenuated in bainiku-ekisu group with Ang II infusion. Bainiku-ekisu further attenuated aortic induction of collagen producing cells and immune cell infiltration. Development of hypertension induced by Ang II was also prevented by bainiku-ekisu.
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Go Mecha Ball coming to Xbox Game PassSuper Rare Games has announced that its chaotic robot-infused game, Go Mecha Ball, will be coming to Xbox Series X|S, Xbox One, and Xbox Game Pass.
Go Mecha Ball coming to Xbox Game PassSuper Rare Games has announced that its chaotic robot-infused game, Go Mecha Ball, will be coming to Xbox Series X|S, Xbox One, and Xbox Game Pass.
Weiterlesen »
 The benefit of vegetarian diets for reducing blood pressure in Taiwan: a historically prospective cohort study - Journal of Health, Population and NutritionObjective Past vegetarians research has often found that they have lower blood pressure (BP). Effects may include their lower BMI and higher intake levels of fruit and vegetables. Besides, the study pursues to extend this evidence in a diverse population containing vegans, lacto-ovo vegetarians and omnivores. Design The study analyzed data on five hundred vigorous individuals aged 20 years or older from a standard medical screening program and provided validated questionnaire. Criteria were established for vegan, lacto-ovo vegetarian, partial vegetarian and omnivorous dietary patterns. Setting Health screening programs were conducted at a standard medical screening program in Taiwan between 2006 and 2017. Dietary data were gathered by self-administered questionnaire. Subjects Five hundred Taiwanese subjects representing the cohort. Results Multiple regression analyses confirmed that the vegan vegetarians had lower systolic and diastolic BP (mmHg) than omnivorous Taiwanese (β = − 6.8, p 139 mmHg or diastolic BP | 89 mmHg or routine of antihypertensive medications, the odds ratio of hypertension compared with omnivores was 0.37 (95% CI = 0.19–0.74), 0.57 (95% CI = 0.36–0.92) and 0.92 (95% CI = 0.50–1.70), respectively, for vegans, lacto-ovo vegetarians and partial vegetarians. Results were reduced after adjustment for BMI. Conclusions The study concludes from this relatively large study that vegetarians, especially vegans, with otherwise diverse characteristics but stable diets, do have lower systolic and diastolic BP and less hypertension than omnivores.
The benefit of vegetarian diets for reducing blood pressure in Taiwan: a historically prospective cohort study - Journal of Health, Population and NutritionObjective Past vegetarians research has often found that they have lower blood pressure (BP). Effects may include their lower BMI and higher intake levels of fruit and vegetables. Besides, the study pursues to extend this evidence in a diverse population containing vegans, lacto-ovo vegetarians and omnivores. Design The study analyzed data on five hundred vigorous individuals aged 20 years or older from a standard medical screening program and provided validated questionnaire. Criteria were established for vegan, lacto-ovo vegetarian, partial vegetarian and omnivorous dietary patterns. Setting Health screening programs were conducted at a standard medical screening program in Taiwan between 2006 and 2017. Dietary data were gathered by self-administered questionnaire. Subjects Five hundred Taiwanese subjects representing the cohort. Results Multiple regression analyses confirmed that the vegan vegetarians had lower systolic and diastolic BP (mmHg) than omnivorous Taiwanese (β = − 6.8, p 139 mmHg or diastolic BP | 89 mmHg or routine of antihypertensive medications, the odds ratio of hypertension compared with omnivores was 0.37 (95% CI = 0.19–0.74), 0.57 (95% CI = 0.36–0.92) and 0.92 (95% CI = 0.50–1.70), respectively, for vegans, lacto-ovo vegetarians and partial vegetarians. Results were reduced after adjustment for BMI. Conclusions The study concludes from this relatively large study that vegetarians, especially vegans, with otherwise diverse characteristics but stable diets, do have lower systolic and diastolic BP and less hypertension than omnivores.
Weiterlesen »
 Bradykinin B2 receptor blockade and intradialytic hypotension - BMC NephrologyIntroduction Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is a common clinical complication and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD). The pathogenesis of IDH has been attributed to the rapid reduction of plasma volume during hemodialysis and the inadequate compensatory mechanisms in response to hypovolemia, such as the lack of vasoconstriction. This may be due to the increased production of vasodilators, such as bradykinin. In this study we test the hypothesis that bradykinin B2 receptor blockade prevents intradialytic hypotension. Methods We performed a post-hoc analysis of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, 2 × 2 crossover clinical trial comparing the continuous infusion of icatibant, a bradykinin B2 receptor blocker, and placebo during hemodialysis. Icatibant or placebo was infused for 30 min before and during hemodialysis in 11 patients on MHD. Results Seven of the patients had IDH, defined as a reduction of systolic blood pressure equal to or greater than 20 mmHg during hemodialysis. Stratified analysis, based on the presence of IDH, revealed that icatibant prevented the decrease in blood pressure compared to placebo in patients with IDH [blood pressure at average nadir (2.5 h after hemodialysis): Placebo,114.3 ± 8.9 vs. icatibant, 125.6 ± 9.1 mmHg, mean ± S.E.M]. Icatibant did not affect blood pressure in the group of patients without IDH. Conclusion Bradykinin B2 receptor blocker may prevent the occurrence of IDH. Further studies should evaluate the hemodynamic effects of icatibant during hemodialysis and the symptomatology associated with IDH.
Bradykinin B2 receptor blockade and intradialytic hypotension - BMC NephrologyIntroduction Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is a common clinical complication and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD). The pathogenesis of IDH has been attributed to the rapid reduction of plasma volume during hemodialysis and the inadequate compensatory mechanisms in response to hypovolemia, such as the lack of vasoconstriction. This may be due to the increased production of vasodilators, such as bradykinin. In this study we test the hypothesis that bradykinin B2 receptor blockade prevents intradialytic hypotension. Methods We performed a post-hoc analysis of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, 2 × 2 crossover clinical trial comparing the continuous infusion of icatibant, a bradykinin B2 receptor blocker, and placebo during hemodialysis. Icatibant or placebo was infused for 30 min before and during hemodialysis in 11 patients on MHD. Results Seven of the patients had IDH, defined as a reduction of systolic blood pressure equal to or greater than 20 mmHg during hemodialysis. Stratified analysis, based on the presence of IDH, revealed that icatibant prevented the decrease in blood pressure compared to placebo in patients with IDH [blood pressure at average nadir (2.5 h after hemodialysis): Placebo,114.3 ± 8.9 vs. icatibant, 125.6 ± 9.1 mmHg, mean ± S.E.M]. Icatibant did not affect blood pressure in the group of patients without IDH. Conclusion Bradykinin B2 receptor blocker may prevent the occurrence of IDH. Further studies should evaluate the hemodynamic effects of icatibant during hemodialysis and the symptomatology associated with IDH.
Weiterlesen »
 Molecular characterization of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from citrus fruit reveals its crucial roles in anthocyanin accumulation - BMC Plant BiologyBackground Flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H), a key enzyme in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, plays an important role in the regulation of flavonols and anthocyanidins accumulation. Citrus fruit is a rich source of flavonoids with varied flavonoid compositions among different varieties. To date, the study on F3H is limited in citrus, and its roles in regulating flavonoid accumulation in citrus fruit are still unclear. Results In this study, we isolated a CitF3H from three different citrus varieties, Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.), Ponkan mandarin (C. reticulata Blanco) and blood orange ‘Moro’ (C. sinensis Osbeck). Functional analysis showed that CitF3H encoded a functional flavanone 3-hydroxylase. It catalyzed the hydroxylation of naringenin to yield dihydrokaempferol, which was a precursor of anthocyanins in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. In the juice sacs, CitF3H was differentially expressed among the three citrus varieties, and its expression level was positively correlated with the accumulation of anthocyanins during the ripening process. In the juice sacs of Satsuma mandarin and Ponkan mandarin the expression of CitF3H kept constant at an extremely low level, and no anthocyanin was accumulated during the ripening process. In contrast, the expression of CitF3H increased rapidly along with the accumulation of anthocyanin in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ during the ripening process. In addition, we found that blue light irradiation was effective to up-regulate the expression of CitF3H and improve anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ in vitro. Conclusion CitF3H was a key gene regulating anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of citrus fruit. The results presented in this study will contribute to elucidating anthocyanin biosynthesis in citrus fruit, and provide new strategies to improve the nutritional and commercial values of citrus fruit.
Molecular characterization of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from citrus fruit reveals its crucial roles in anthocyanin accumulation - BMC Plant BiologyBackground Flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H), a key enzyme in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, plays an important role in the regulation of flavonols and anthocyanidins accumulation. Citrus fruit is a rich source of flavonoids with varied flavonoid compositions among different varieties. To date, the study on F3H is limited in citrus, and its roles in regulating flavonoid accumulation in citrus fruit are still unclear. Results In this study, we isolated a CitF3H from three different citrus varieties, Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.), Ponkan mandarin (C. reticulata Blanco) and blood orange ‘Moro’ (C. sinensis Osbeck). Functional analysis showed that CitF3H encoded a functional flavanone 3-hydroxylase. It catalyzed the hydroxylation of naringenin to yield dihydrokaempferol, which was a precursor of anthocyanins in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. In the juice sacs, CitF3H was differentially expressed among the three citrus varieties, and its expression level was positively correlated with the accumulation of anthocyanins during the ripening process. In the juice sacs of Satsuma mandarin and Ponkan mandarin the expression of CitF3H kept constant at an extremely low level, and no anthocyanin was accumulated during the ripening process. In contrast, the expression of CitF3H increased rapidly along with the accumulation of anthocyanin in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ during the ripening process. In addition, we found that blue light irradiation was effective to up-regulate the expression of CitF3H and improve anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of blood orange ‘Moro’ in vitro. Conclusion CitF3H was a key gene regulating anthocyanin accumulation in the juice sacs of citrus fruit. The results presented in this study will contribute to elucidating anthocyanin biosynthesis in citrus fruit, and provide new strategies to improve the nutritional and commercial values of citrus fruit.
Weiterlesen »
 Netflix's They Cloned Tyrone will make you think twice about eating fried chicken againNetflix wants you to really think hard about ordering fried chicken ever again
Netflix's They Cloned Tyrone will make you think twice about eating fried chicken againNetflix wants you to really think hard about ordering fried chicken ever again
Weiterlesen »
 Bamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extractsBamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extracts antioxidants_OA UniCalPortale bamboo leaf sheath extract antoxidant antiinfammatory
Bamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extractsBamboo's hidden treasures: unveiling the possible health-boosting powers of leaf and sheath extracts antioxidants_OA UniCalPortale bamboo leaf sheath extract antoxidant antiinfammatory
Weiterlesen »