Erin McCarthy '23, physics summa cum laude, is a rarity among young scientists. As an undergraduate researcher in Syracuse University's College of Arts & Sciences' Department of Physics, she guided a study that appeared in March 2024 in Physical Review Letters.
Mar 22 2024Syracuse University Erin McCarthy '23, physics summa cum laude, is a rarity among young scientists. As an undergraduate researcher in Syracuse University's College of Arts & Sciences' Department of Physics, she guided a study that appeared in March 2024 in Physical Review Letters. It is the most-cited physics letters journal and the eighth-most cited journal in science overall.
M. Lisa Manning, co-author, the William R. Kenan, Jr. Professor of Physics and founding director of the BioInspired Institute at Syracuse University The research team used computational physics modeling to figure out the underlying mechanisms that cause particles to sort spontaneously into different groups.
Related StoriesPrevious physics investigations found that particles separate when some receive a jolt of higher temperature. As one population of particles becomes injected with energy at a small scale, it turns active-;or "hot"-;while the other population is left inactive, or "cold." This difference in heat causes a reorganization among the two populations.
"Your skin, for instance, is a very dense environment," said McCarthy. "Cells are packed so closely together, there's no space between them. If we want to apply these physics findings to biology, we must look at high densities for our models to be applicable. But at very high densities, the difference in activity between two populations does not cause them to sort."
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 AI language model provides new insights into the development of brain diseasesA new AI language model identifies clinical symptoms in medical summaries and links them to brain tissue from donors of the Netherlands Brain Bank. This yields new insights into the development of individual disease progression and contributes to a better understanding of common misdiagnoses of brain diseases.
AI language model provides new insights into the development of brain diseasesA new AI language model identifies clinical symptoms in medical summaries and links them to brain tissue from donors of the Netherlands Brain Bank. This yields new insights into the development of individual disease progression and contributes to a better understanding of common misdiagnoses of brain diseases.
Weiterlesen »
 Vertex 2024 speaker: learn insights from Dolph Souza's 3D workflowJoe is a regular freelance journalist and editor at Creative Bloq. He writes news and features, updates buying guides and keeps track of the best equipment for creatives, from monitors to accessories and office supplies.
Vertex 2024 speaker: learn insights from Dolph Souza's 3D workflowJoe is a regular freelance journalist and editor at Creative Bloq. He writes news and features, updates buying guides and keeps track of the best equipment for creatives, from monitors to accessories and office supplies.
Weiterlesen »
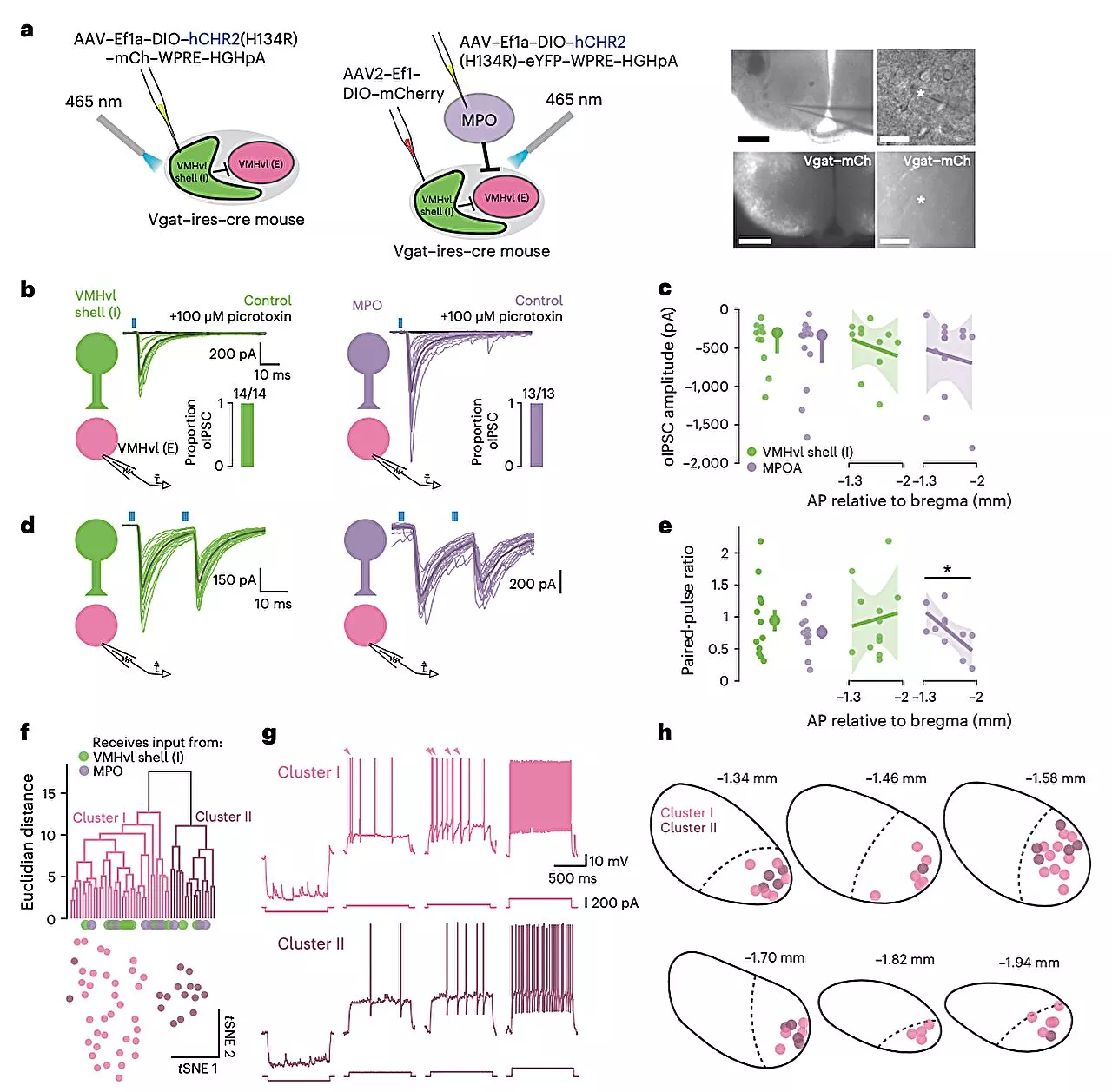 Study offers insights into neural mechanisms involved in progression from aggressive motivation to actionThe social behaviors of humans and animals often unfold over two distinct phases, namely a motivational and an action phase. The first of these phases entails instinctual and reward-seeking mental states, characterized by sexual or aggressive drives to perform specific actions. The second phase entails acting on these motivations and drives.
Study offers insights into neural mechanisms involved in progression from aggressive motivation to actionThe social behaviors of humans and animals often unfold over two distinct phases, namely a motivational and an action phase. The first of these phases entails instinctual and reward-seeking mental states, characterized by sexual or aggressive drives to perform specific actions. The second phase entails acting on these motivations and drives.
Weiterlesen »
 New insights on the brain's emotional processing centerHow much do our emotions depend on our senses? Does our brain and body react in the same way when we hear a fearful scream, see an eerie shadow, or smell a sinister odor? And does hearing an upbeat music or seeing a colorful landascape bring the same...
New insights on the brain's emotional processing centerHow much do our emotions depend on our senses? Does our brain and body react in the same way when we hear a fearful scream, see an eerie shadow, or smell a sinister odor? And does hearing an upbeat music or seeing a colorful landascape bring the same...
Weiterlesen »
 New study defines clinical phenotype of Post-infectious ME/CFS, highlighting unique biomarker insightsThe pathophysiological mechanisms of PI myalgic encephalitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
New study defines clinical phenotype of Post-infectious ME/CFS, highlighting unique biomarker insightsThe pathophysiological mechanisms of PI myalgic encephalitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
Weiterlesen »
 Vertex 2024 speaker: gain insights from Alina Fedaseyenka's art for SynapseJoe is a regular freelance journalist and editor at Creative Bloq. He writes news and features, updates buying guides and keeps track of the best equipment for creatives, from monitors to accessories and office supplies.
Vertex 2024 speaker: gain insights from Alina Fedaseyenka's art for SynapseJoe is a regular freelance journalist and editor at Creative Bloq. He writes news and features, updates buying guides and keeps track of the best equipment for creatives, from monitors to accessories and office supplies.
Weiterlesen »
