In a new study, clinician-scientists and researchers from the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS) have demonstrated the use of exosomes to successfully target squamous cell cancer tumours that are usually resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
National Cancer Centre SingaporeSep 2 2024 In a new study, clinician-scientists and researchers from the National Cancer Centre Singapore have demonstrated the use of exosomes to successfully target squamous cell cancer tumours that are usually resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors . Their research is the first where exosomes have been applied to target TKI-resistant cancers in Singapore. The findings were published in the journal Developmental Cell last month.
The discovery One of the biggest groups of EGFR-implicated cancers are squamous cell cancers, one of the deadliest cancers worldwide. Professor Gopal Iyer, Head of the Department of Head and Neck Surgery, Division of Surgery and Surgical Oncology, Singapore General Hospital and NCCS, treats head and neck squamous cell cancers in which over 80-90% of tumours have overexpressed EGFR.
Exosomes, which are excreted by all living cells, contains cell parts such as DNA, RNA, lipids, and proteins. They secreted into circulation and affect the function and behaviour of other cells they encounter. This communication has been shown to influence the development of various diseases including inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative diseases and cancer, which has made using exosomes a new and promising field for medical treatments.
Opening a treasure chest On what this means for patients, Professor Iyer, who is also Head of the translational research Division of Medical Sciences at NCCS commented, "Our findings provide new hope for patients as we can potentially target a large population who previously had poor prognosis for their cancer. We're excited to partner industry to move this research to the next phase so that we can start offering therapeutic solutions to our patients in the clinic.
Exosomes Living Cells Biomarker Cell Drugs Growth Factor Head And Neck Cancer Healthcare Hospital Kinase Medical Research Neck Oncology Proton Therapy Receptor Research RNA Surgery Therapeutics Tyrosine
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Study finds breast cancer screening attendance helps boost other cancer screeningsOffering self-sampling kits to women overdue for cervical cancer (CC) or colorectal cancer (CRC) screening when they attend breast cancer (BC) screening can result in increased screening participation, according to a study published online Aug. 13 in PLOS Medicine.
Study finds breast cancer screening attendance helps boost other cancer screeningsOffering self-sampling kits to women overdue for cervical cancer (CC) or colorectal cancer (CRC) screening when they attend breast cancer (BC) screening can result in increased screening participation, according to a study published online Aug. 13 in PLOS Medicine.
Weiterlesen »
 The Greater Manchester village at the centre of a national problem'I don't know if it could take any more'
The Greater Manchester village at the centre of a national problem'I don't know if it could take any more'
Weiterlesen »
 French National Centre for Scientific ResearchThe CNRS has over 80 years experience of basic research, exploring living creatures, space, materials and human societies and can leverage all fields of science to understand current global challenges in all their complexity, in conjunction with organisations in the field.
French National Centre for Scientific ResearchThe CNRS has over 80 years experience of basic research, exploring living creatures, space, materials and human societies and can leverage all fields of science to understand current global challenges in all their complexity, in conjunction with organisations in the field.
Weiterlesen »
 Half of cancer survivors face cancer-related financial hardshipHalf of cancer survivors experience cancer-related financial hardship, according to a research letter published online Aug. 20 in JAMA Network Open.
Half of cancer survivors face cancer-related financial hardshipHalf of cancer survivors experience cancer-related financial hardship, according to a research letter published online Aug. 20 in JAMA Network Open.
Weiterlesen »
 Targeted cancer cell therapy may slow endometrial cancerThere may be a way to slow the growth of endometrial cancer through targeted cancer cell therapy, according to new research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
Targeted cancer cell therapy may slow endometrial cancerThere may be a way to slow the growth of endometrial cancer through targeted cancer cell therapy, according to new research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
Weiterlesen »
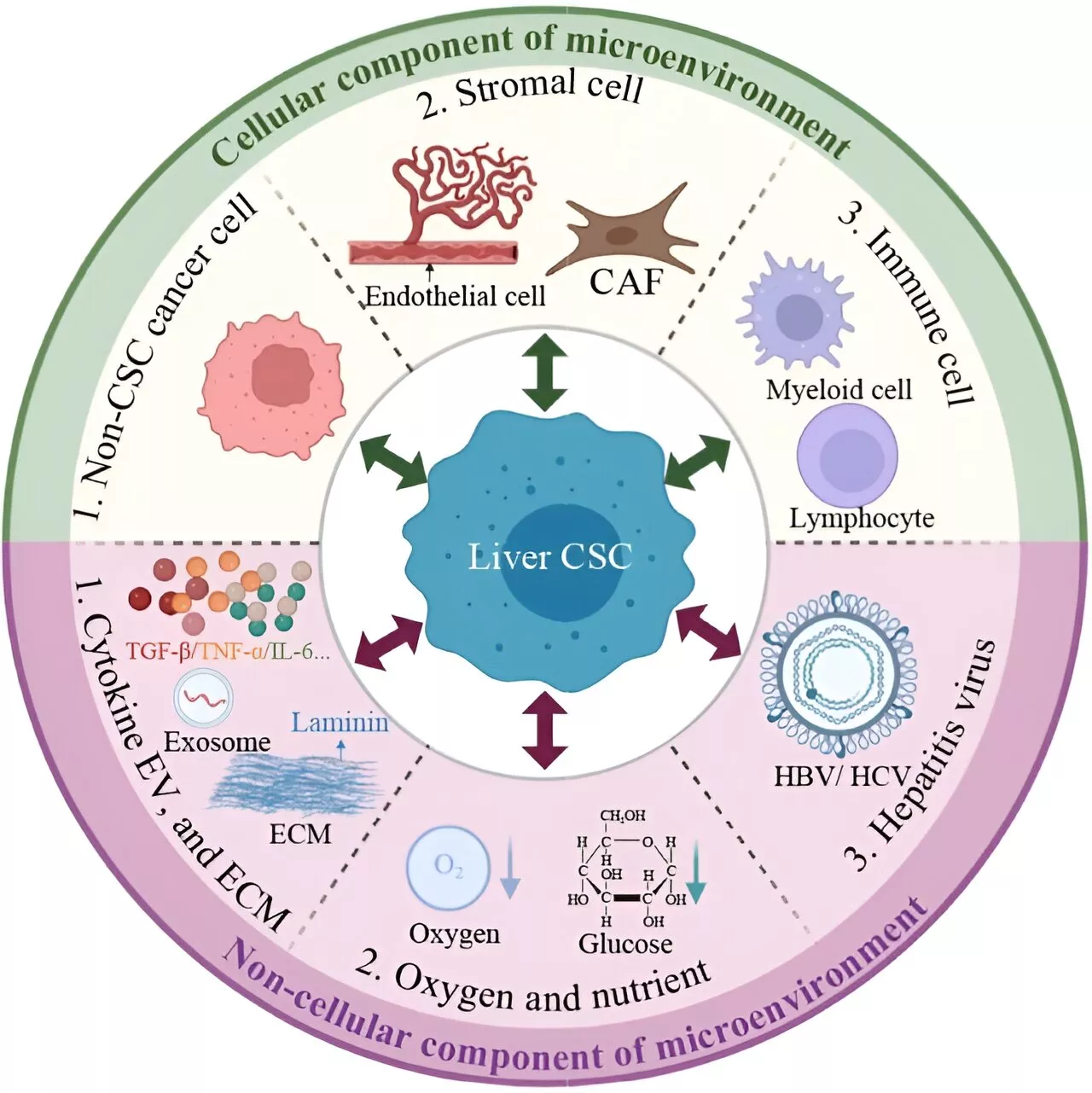 Cancer stem cell-immune cell crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment for liver cancer progressionThe complex dynamics between liver cancer stem cells (CSCs) and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME) are central to the progression of liver cancer. These interactions are critical in creating an immunosuppressive setting that significantly impacts the response to immunotherapy.
Cancer stem cell-immune cell crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment for liver cancer progressionThe complex dynamics between liver cancer stem cells (CSCs) and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME) are central to the progression of liver cancer. These interactions are critical in creating an immunosuppressive setting that significantly impacts the response to immunotherapy.
Weiterlesen »