Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is thrilled to announce its Polycystic Kidney Disease Outcomes Consortium (PKDOC) has been awarded an Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease (ADTKD) focused Broad Agency Announcement (BAA) contract from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Critical Path Institute Sep 24 2024 Critical Path Institute is thrilled to announce its Polycystic Kidney Disease Outcomes Consortium has been awarded an Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease focused Broad Agency Announcement contract from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
ADTKD only affects the kidney, resulting in slowly worsening kidney function and the need for dialysis or kidney transplant at an average age of 45 years. It is caused predominantly by genetic changes in the UMOD and MUC1 genes. Because of the inheritance pattern , a child of an affected parent has a 50% chance of also being affected. Thus, many family members have kidney disease and will eventually need a kidney transplant or dialysis.
Given its recent identification as a cause of kidney disease and its rarity, little is known about factors that affect progression of kidney disease in ADTKD. Understanding rates of progression is important for patients and important for the development of future clinical trials. C-Path will now play a major role in analyzing available clinical data about ADTKD and helping to better understand the factors associated with disease progression.
We are very grateful for the support we have received from FDA to pursue this important project. This proposal represents our commitment to advancing the quantitative understanding of ADTKD progression through incorporation of relevant biomarkers into disease progression models, thus allowing a path forward for more efficient clinical trials and eventual drug approvals for this devastating disease.
Kidney Dialysis Food Genes Genetic Kidney Disease Kidney Transplant Laboratory Ph Polycystic Kidney Disease Transplant
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Homelessness linked to end-stage kidney disease, death in veterans with incident chronic kidney diseaseFor veterans with incident chronic kidney disease (CKD), a history of homelessness is associated with an increased risk for end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) and death, according to a study published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Network Open.
Homelessness linked to end-stage kidney disease, death in veterans with incident chronic kidney diseaseFor veterans with incident chronic kidney disease (CKD), a history of homelessness is associated with an increased risk for end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) and death, according to a study published online Sept. 10 in JAMA Network Open.
Weiterlesen »
 Breakthrough research identifies key microenvironments linked to kidney injury and diseaseA study published in Nature Communications provides new insight into how damaged cells interact within disease-promoting microenvironments following acute kidney injury, or AKI.
Breakthrough research identifies key microenvironments linked to kidney injury and diseaseA study published in Nature Communications provides new insight into how damaged cells interact within disease-promoting microenvironments following acute kidney injury, or AKI.
Weiterlesen »
 Guidance provided for management of obesity in kidney diseaseIn a report issued by the American Society of Nephrology and published online Sept. 18 in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, guidance is presented for the management of obesity in persons with kidney disease.
Guidance provided for management of obesity in kidney diseaseIn a report issued by the American Society of Nephrology and published online Sept. 18 in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, guidance is presented for the management of obesity in persons with kidney disease.
Weiterlesen »
 Genetic analysis sheds light on the role of IFT140 in polycystic kidney diseasePolycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an intractable disorder that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. It is typically seen in adults. As one of the most prevalent hereditary kidney diseases, the autosomal dominant form of PKD is usually caused by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes.
Genetic analysis sheds light on the role of IFT140 in polycystic kidney diseasePolycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an intractable disorder that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. It is typically seen in adults. As one of the most prevalent hereditary kidney diseases, the autosomal dominant form of PKD is usually caused by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes.
Weiterlesen »
 Addressing the challenges of polycystic kidney diseasePolycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an intractable disorder that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. It is typically seen in adults. As one of the most prevalent hereditary kidney diseases, the autosomal dominant form of PKD is usually caused by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes.
Addressing the challenges of polycystic kidney diseasePolycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an intractable disorder that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. It is typically seen in adults. As one of the most prevalent hereditary kidney diseases, the autosomal dominant form of PKD is usually caused by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes.
Weiterlesen »
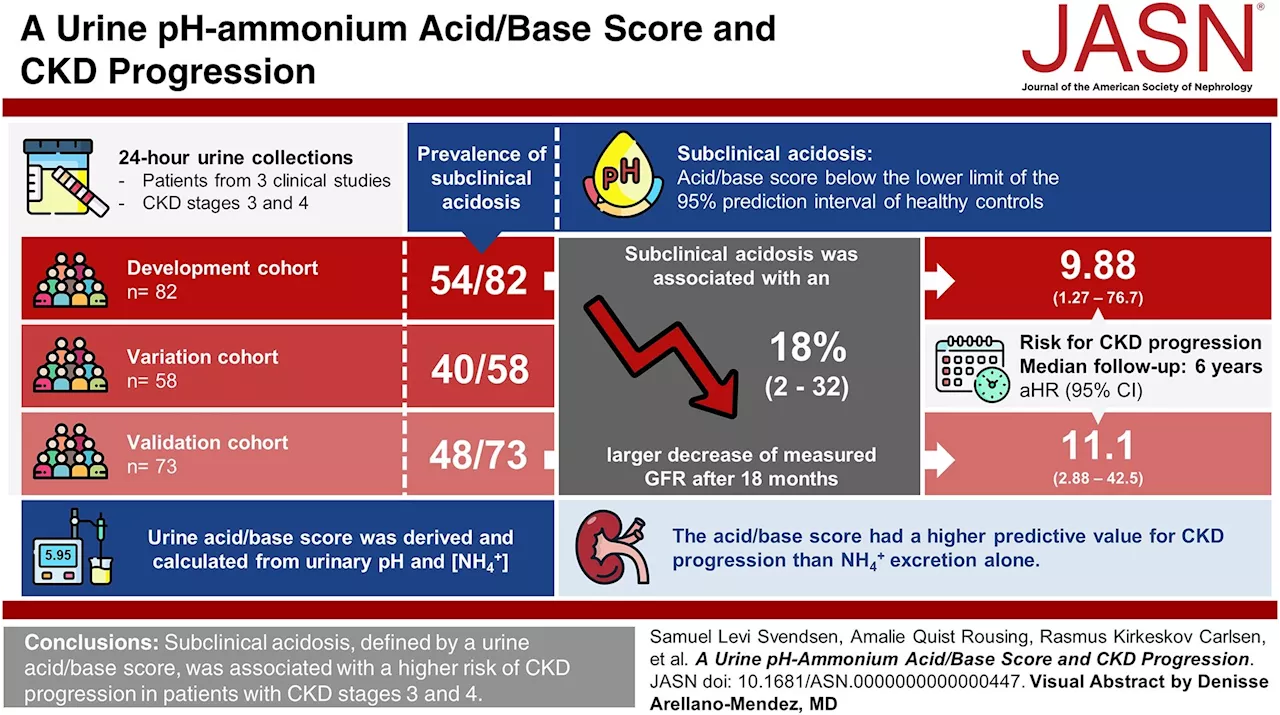 New method predicts worsening of chronic kidney diseaseResearchers from Aarhus University have developed a new method to predict which patients with chronic kidney failure are at risk of losing kidney function over time. The method is based on an analysis of acid-base balances in urine samples, which can reveal early signs of acid buildup—a condition that can be harmful to kidney function.
New method predicts worsening of chronic kidney diseaseResearchers from Aarhus University have developed a new method to predict which patients with chronic kidney failure are at risk of losing kidney function over time. The method is based on an analysis of acid-base balances in urine samples, which can reveal early signs of acid buildup—a condition that can be harmful to kidney function.
Weiterlesen »