Multiple recurrent, repeat expansions found in human cancer genomes nature
. A repeat expansion was called when the repeat tract length for one allele of the tumour sample was greater than 100 bp and exceeded the repeat tract length of both normal alleles. A locus was considered validated if at least ten cancer genomes had a repeat expansion.Twelve pairs of matching normal and tumour samples from patients with clear cell RCC were obtained with the patients’ informed consent ex vivo upon surgical tumour resection and analysed.
We benchmarked the local read depth filter in silico by observing its behaviour with simulated reads. First, we created a reference genome containing artificially expanded repeats. We randomly selected ten TRs located on chromosome 1 that were shorter than the sequencing read length of 100 bp. We artificially expanded these TRs on chromosome 1 of GRCh37 with the BioPython Python package .
To simulate copy number amplification, the read simulation process was repeated using reference files that contained only the artificially expanded repeats and their surrounding 1,000-bp flanking regions. We created ten pairs of fastq files, each with an increasing copy number. We specified the copy number by multiplying the number of reads to generate by the required number.
The base fastq file with a copy number of 2, in addition to the eight copy number-amplified fastq files, was aligned to chromosome 1 of GRCh37 with bwa-mem with the default options. The resulting SAM files were converted to BAM format with samtools using the default options. Finally, we ran the EHdn profile command with the minimum anchor mapping quality set to 50 and maximum IRR mapping quality set to 40.
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
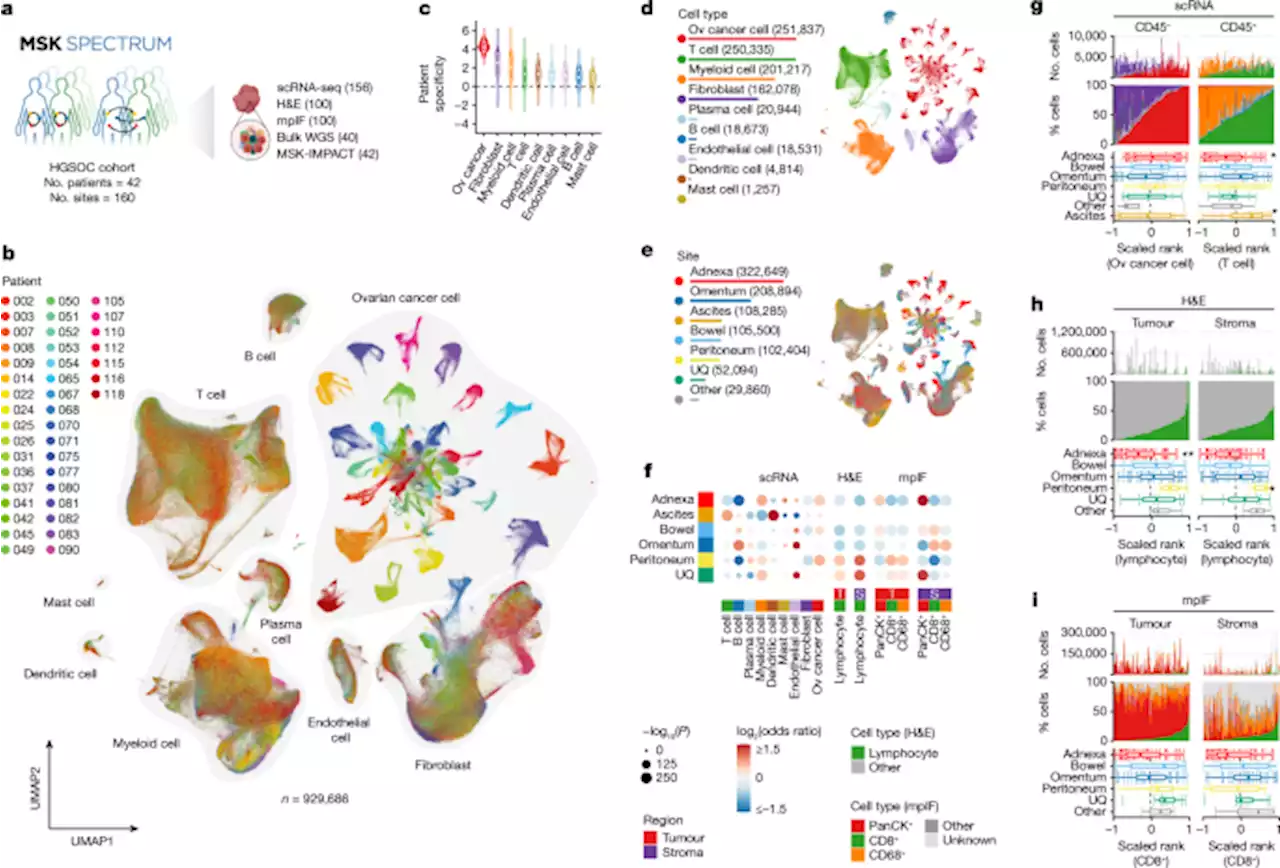 Ovarian cancer mutational processes drive site-specific immune evasion - NatureMulti-modal analysis of genomically unstable ovarian tumours characterizes the contribution of anatomical sites and mutational processes to evolutionary phenotypic divergence and immune resistance mechanisms.
Ovarian cancer mutational processes drive site-specific immune evasion - NatureMulti-modal analysis of genomically unstable ovarian tumours characterizes the contribution of anatomical sites and mutational processes to evolutionary phenotypic divergence and immune resistance mechanisms.
Weiterlesen »
 Breast cancer cells survive chemotherapy by activating targetable immune-modulatory programs characterized by PD-L1 or CD80 - Nature CancerShahbandi et al. find that cancer cells that survive chemotherapy (CT) activate two immune-modulatory programs characterized by IFN response genes and CD274 or p53 signaling and CD80 expression. Targeting these pathways enhances the CT response.
Breast cancer cells survive chemotherapy by activating targetable immune-modulatory programs characterized by PD-L1 or CD80 - Nature CancerShahbandi et al. find that cancer cells that survive chemotherapy (CT) activate two immune-modulatory programs characterized by IFN response genes and CD274 or p53 signaling and CD80 expression. Targeting these pathways enhances the CT response.
Weiterlesen »
 Manchester's Kenworthy Woods: Former tip declared nature reserveKenworthy Woods, which was transformed in the 1990s, becomes Manchester's ninth local nature reserve
Manchester's Kenworthy Woods: Former tip declared nature reserveKenworthy Woods, which was transformed in the 1990s, becomes Manchester's ninth local nature reserve
Weiterlesen »
 Pathogenic variants in SLF2 and SMC5 cause segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy - Nature CommunicationsThe SMC5/6 complex is critical for genome stability. Here, the authors identify mutations in SLF2 and SMC5 as cause of Atelís Syndrome characterized by microcephaly, short stature, anemia, segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy.
Pathogenic variants in SLF2 and SMC5 cause segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy - Nature CommunicationsThe SMC5/6 complex is critical for genome stability. Here, the authors identify mutations in SLF2 and SMC5 as cause of Atelís Syndrome characterized by microcephaly, short stature, anemia, segmented chromosomes and mosaic variegated hyperploidy.
Weiterlesen »
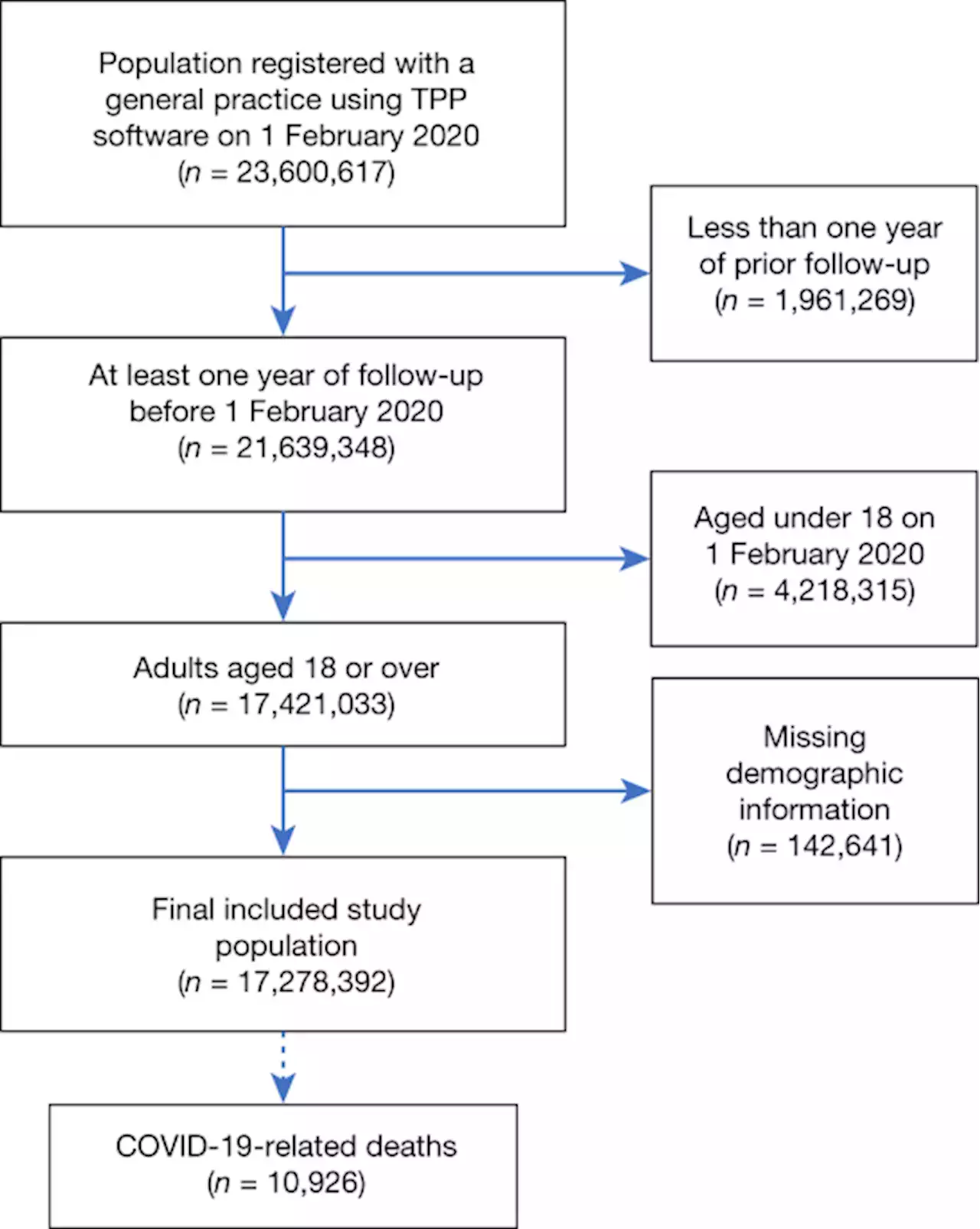 Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY - NatureOpenSAFELY, a new health analytics platform that includes data from over 17 million adult NHS patients in England, is used to examine factors associated with COVID-19-related death.
Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY - NatureOpenSAFELY, a new health analytics platform that includes data from over 17 million adult NHS patients in England, is used to examine factors associated with COVID-19-related death.
Weiterlesen »
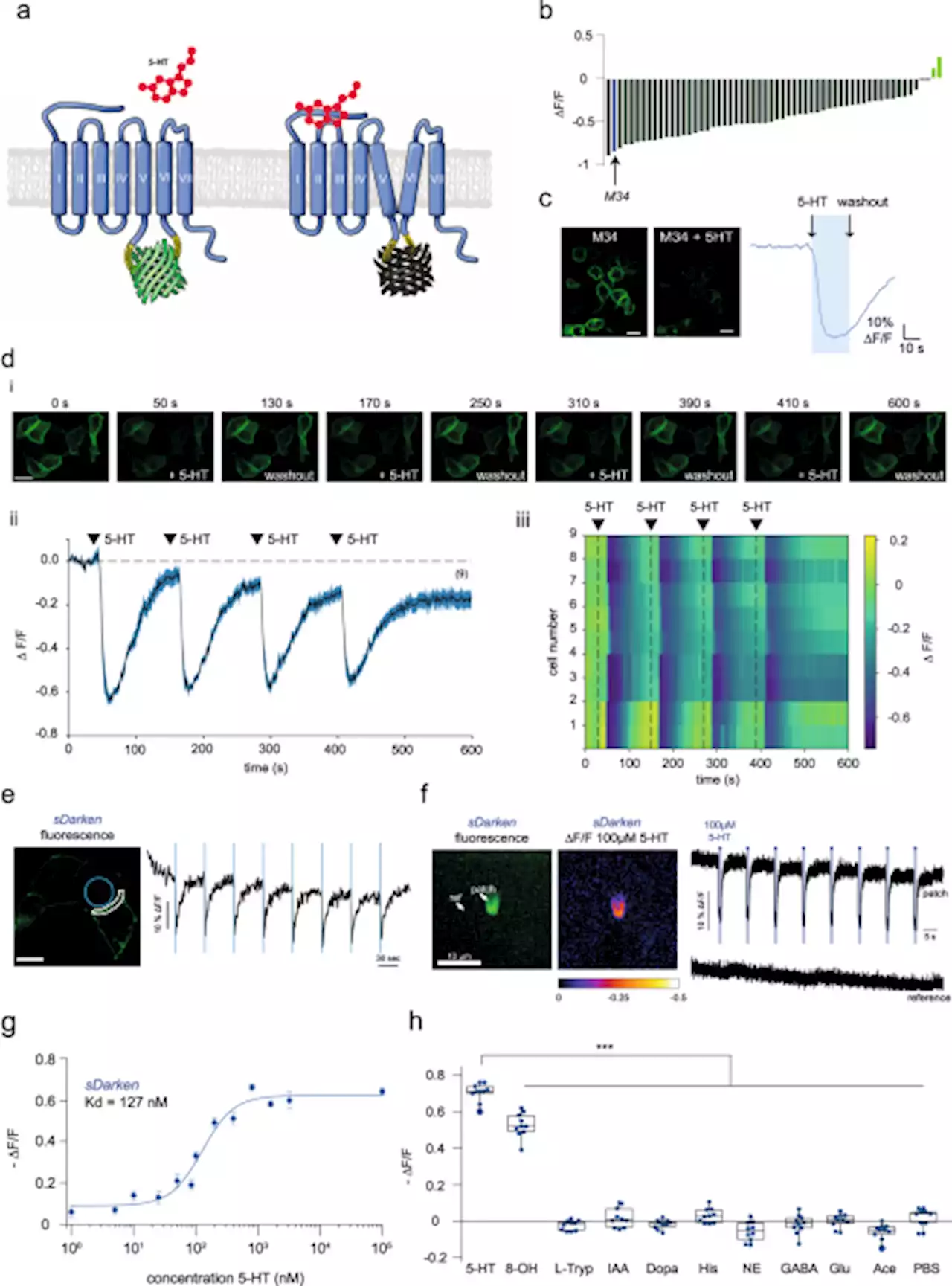 Next generation genetically encoded fluorescent sensors for serotonin - Nature CommunicationsGenetically encoded sensors have been developed and become versatile tools for imaging serotonin dynamics. Here, authors developed a family of serotonin (5-HT) sensors (sDarken), three variants with different affinities for 5-HT enable high spatiotemporal resolution of 5-HT dynamics.
Next generation genetically encoded fluorescent sensors for serotonin - Nature CommunicationsGenetically encoded sensors have been developed and become versatile tools for imaging serotonin dynamics. Here, authors developed a family of serotonin (5-HT) sensors (sDarken), three variants with different affinities for 5-HT enable high spatiotemporal resolution of 5-HT dynamics.
Weiterlesen »
