An international research team has uncovered a new mechanism crucial to the production of cellular proteins.
Goethe University FrankfurtNov 15 2024 When this mechanism is disrupted, the blueprints used by the cell to produce proteins are inaccurately edited through a process called splicing. The study, led by Goethe University Frankfurt, sheds light on how specific mutations may lead to the retinal disease retinitis pigmentosa .
This diversity is enabled by a process known as "splicing." When a cell requires a protein, it generates a copy of the relevant instructions in the cell nucleus. During splicing, this transcript undergoes modification: a cellular editing complex, the spliceosome, removes certain segments. The outcome varies depending on which parts are cut out, resulting in distinct blueprints for different proteins.This process is crucial for the life of the cell.
"We already knew that certain mutations in these subunits are linked to the eye disease retinitis pigmentosa," says Dr. Cristian Prieto-Garcia from the Institute of Biochemistry II, the first author of the study. "What we didn't yet understand was the exact impact of these mutations."In experiments with zebrafish, the team has now managed to fill this knowledge gap.
Cell Death Protein Biochemistry Cancer Cell Nucleus Genes Genome Retinitis Pigmentosa Splicing
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Man born with three penises discovered by student researchersResearchers from the University of Birmingham Medical School stumbled across the “serendipitous discovery” while dissecting the donated body of a 78-year-old man
Man born with three penises discovered by student researchersResearchers from the University of Birmingham Medical School stumbled across the “serendipitous discovery” while dissecting the donated body of a 78-year-old man
Weiterlesen »
 WeChat devs introduced security flaws when they modded TLS, say researchersNo attacks possible, but enough issues to cause concern
WeChat devs introduced security flaws when they modded TLS, say researchersNo attacks possible, but enough issues to cause concern
Weiterlesen »
 Researchers start work to solve mystery of Nottingham gorillaGeorge the gorilla is a local legend but very little is known about him
Researchers start work to solve mystery of Nottingham gorillaGeorge the gorilla is a local legend but very little is known about him
Weiterlesen »
 UZH researchers harness AI to detect antibiotic resistanceResearchers at the University of Zurich (UZH) have used artificial intelligence (AI) to help identify antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
UZH researchers harness AI to detect antibiotic resistanceResearchers at the University of Zurich (UZH) have used artificial intelligence (AI) to help identify antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Weiterlesen »
 Researchers Discover Algorithm to Slash AI Energy Consumption by 95%Researchers have developed a new algorithm that could significantly reduce the energy consumption of AI, offering a potential solution to the industry's growing energy footprint.
Researchers Discover Algorithm to Slash AI Energy Consumption by 95%Researchers have developed a new algorithm that could significantly reduce the energy consumption of AI, offering a potential solution to the industry's growing energy footprint.
Weiterlesen »
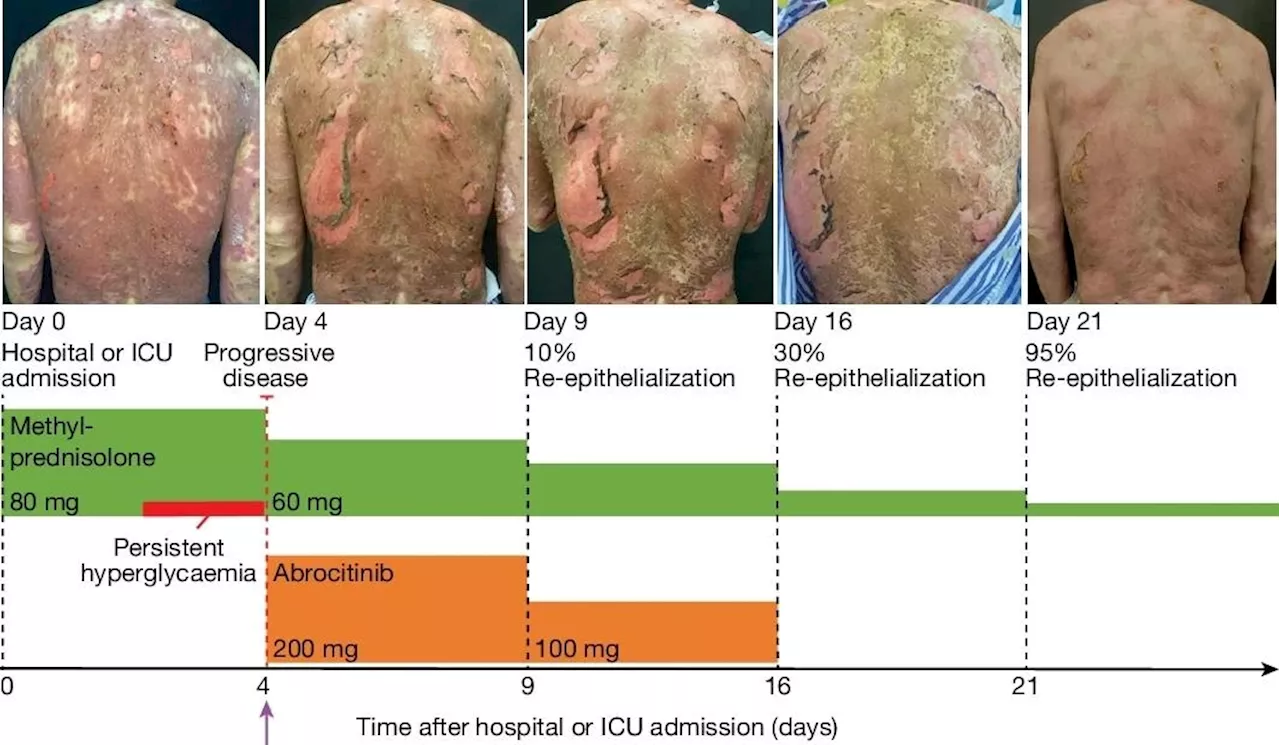 Researchers uncover the potential of JAK inhibitors to treat life-threatening skin diseaseResearchers identified Janus kinase inhibitors as a promising treatment for the severe drug-induced skin condition toxic epidermal necrolysis, by analyzing patient biopsies with deep visual proteomics.
Researchers uncover the potential of JAK inhibitors to treat life-threatening skin diseaseResearchers identified Janus kinase inhibitors as a promising treatment for the severe drug-induced skin condition toxic epidermal necrolysis, by analyzing patient biopsies with deep visual proteomics.
Weiterlesen »