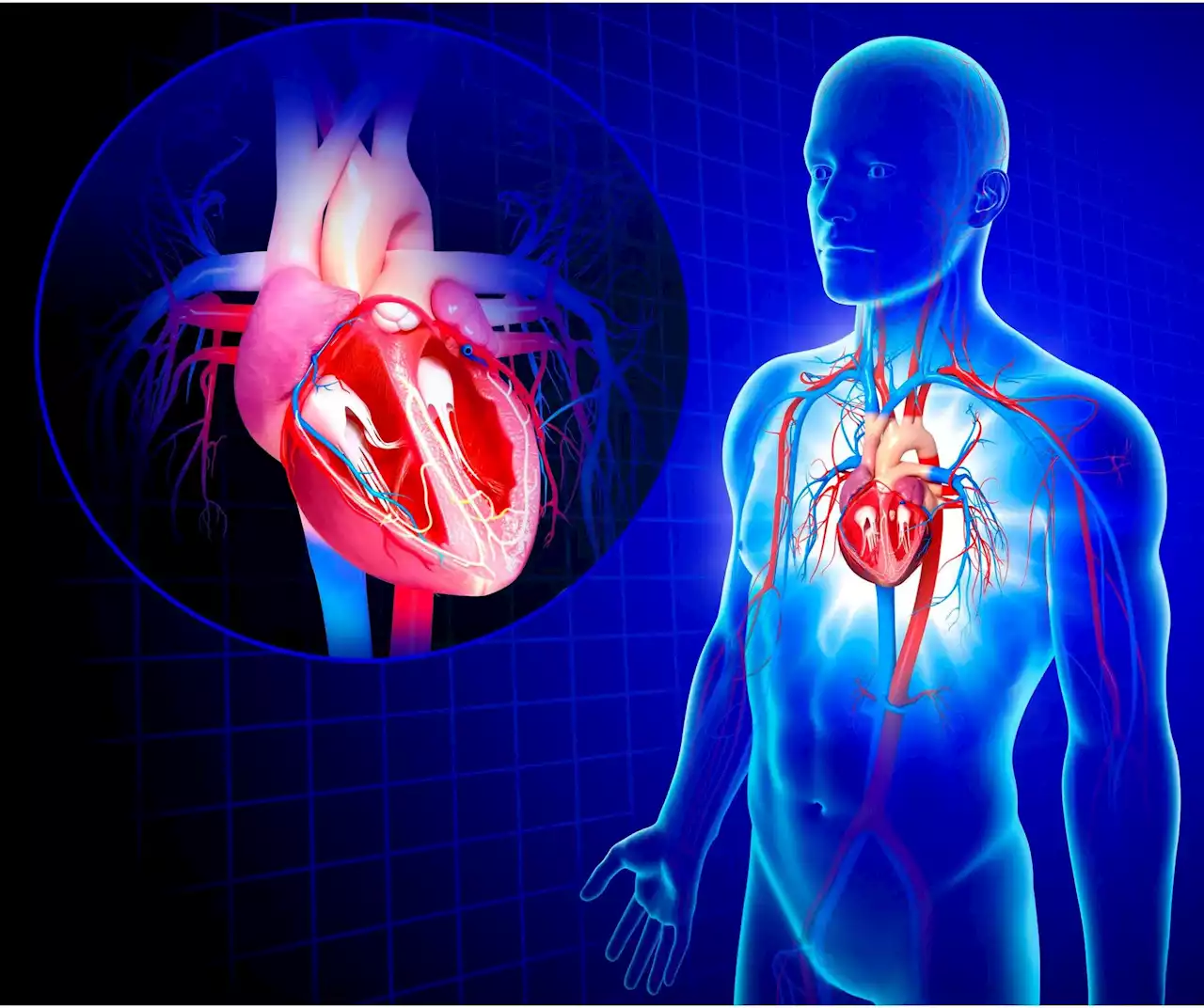
Engineered stem cells do not provoke dangerous heart rhythms, a challenge that has prevented the progress of stem cell transplants for damaged hearts. Researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle have successfully created stem cells that do not cause dangerous arrhythmi
Researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine have successfully engineered stem cells that do not cause dangerous arrhythmias, a major complication previously hindering stem-cell therapies for injured hearts. By using CRISPR-based genome editing to modify ion channels in the stem cells, the team created a new line of cells called “MEDUSA,” which engraft in the heart, mature, and integrate into heart muscle without generating dangerous heart rates.
To create their therapeutic heart cells, the Seattle researchers used pluripotent stem cells. Unlike adult stem cells, which have specialized to become specific cell types, pluripotent stem cells can become any type of cell in the body. But there was one major complication. During the early weeks of engraftment, the hearts tended to beat at a dangerously high rate. Unless a way could be found to prevent or suppress this problem, stem cells could not become a safe treatment for myocardial infarction and heart failure.
In pacemaker cells, the voltage cycles back and forth from negative to positive . Murry compares it to a metronome with positive ions swooshing in and out of the cell through these channels. The rate at which this cycle of repolarization and depolarization occurs determines the heart rate. To determine which ion channels were the culprits carrying the arrhythmia-causing current, the scientists used CRISPR-based genome editing to systematically knock out depolarizing genes or to activate repolarizing genes. This proved surprisingly complex. They had hypothesized that there would be a single ion channel causing the arrhythmia, but none of the single-gene edits eliminated the rapid heart rhythms.
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Easter Sunday is a chance to overcome human doubt, as this apostle did, says Kansas pastorEaster Sunday is a time for imitating the Apostle John and overcoming doubts to embrace Christ's resurrection, Connor Kraus, a Topeka-based pastor, told Fox News Digital.
Easter Sunday is a chance to overcome human doubt, as this apostle did, says Kansas pastorEaster Sunday is a time for imitating the Apostle John and overcoming doubts to embrace Christ's resurrection, Connor Kraus, a Topeka-based pastor, told Fox News Digital.
Weiterlesen »
 Scientists find promising antibiotic-resistant bacteria treatment — goldAntibiotic-resistant bacteria is one of the most pressing public health crises of the coming decades, but an innovative new approach using gold atoms might hold the key to fighting back.
Scientists find promising antibiotic-resistant bacteria treatment — goldAntibiotic-resistant bacteria is one of the most pressing public health crises of the coming decades, but an innovative new approach using gold atoms might hold the key to fighting back.
Weiterlesen »
 Scientists Prove That the Human Body Can Predict MealtimesAccording to a recent study from the University of Surrey, the human body has the ability to predict the timing of regular meals. The findings of the research team suggest that the daily rhythms of blood glucose levels may be influenced not only by the timing of meals but also by their portion sizes
Scientists Prove That the Human Body Can Predict MealtimesAccording to a recent study from the University of Surrey, the human body has the ability to predict the timing of regular meals. The findings of the research team suggest that the daily rhythms of blood glucose levels may be influenced not only by the timing of meals but also by their portion sizes
Weiterlesen »
 Scientists Discover That Ancient Humans Were Tripping Balls in a CaveRecovered human hairs provide the first direct evidence that prehistoric Europeans were fond of consuming psychoactive rugs like scopolamine.
Scientists Discover That Ancient Humans Were Tripping Balls in a CaveRecovered human hairs provide the first direct evidence that prehistoric Europeans were fond of consuming psychoactive rugs like scopolamine.
Weiterlesen »
 Discovery with cancer research impact makes scientists dance in lab'This work will be built upon here and by other researchers worldwide to advance our approach to figuring out ways to target cancers'
Discovery with cancer research impact makes scientists dance in lab'This work will be built upon here and by other researchers worldwide to advance our approach to figuring out ways to target cancers'
Weiterlesen »