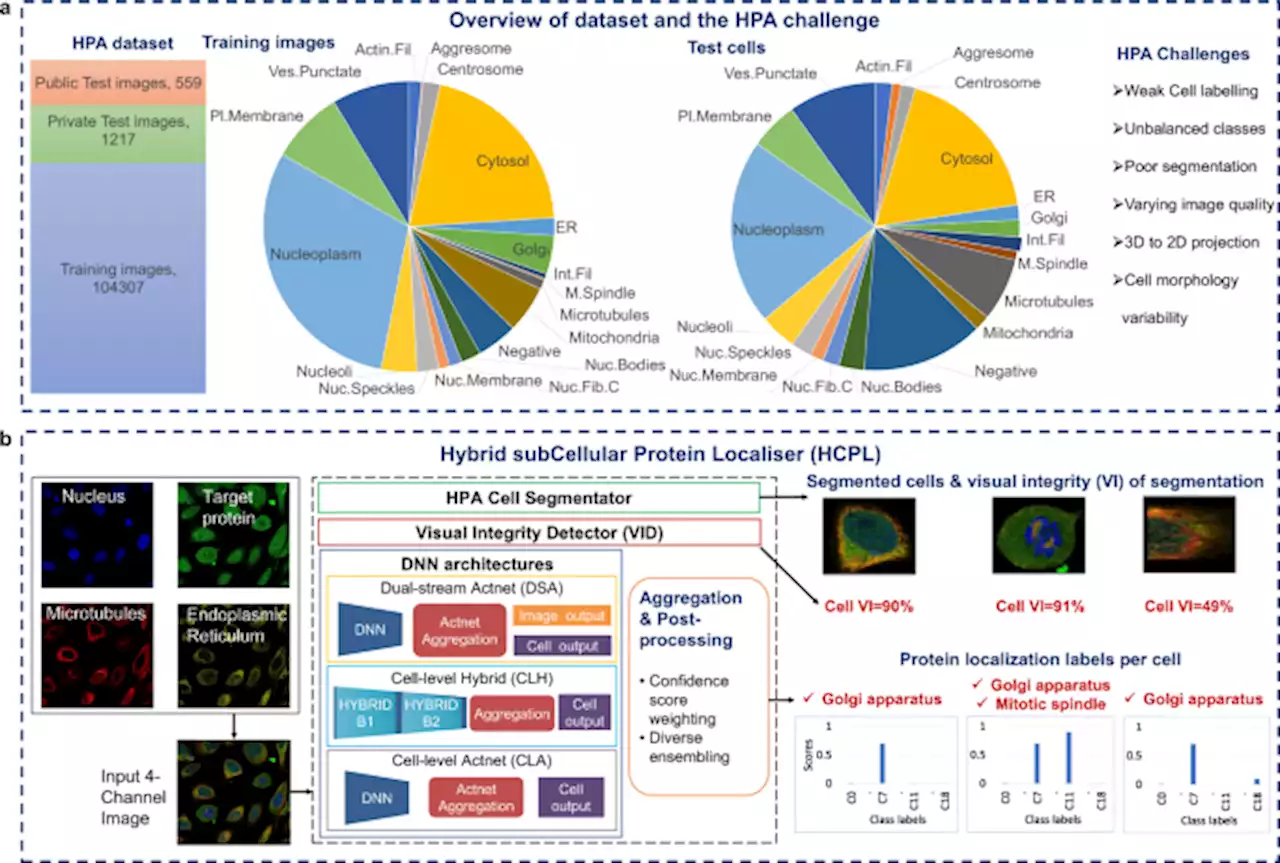
Newly developed AI shows speed and accuracy in identifying the location and expression of proteins uniofsurrey CommsBio
. Here, each point on the plot represents a single cell. Only cells with single labels are chosen, coloured by their respective label.
Fig. 9: Visualisation of the deep features for DSA and CLH DNNs from the UMAP dimensionality reduction method. High-dimensional data is projected onto a 2D plane such that local structures in the original space are captured, whilst simultaneously retaining the global structure of the data. Different subcellular locations are effectively clustered by deep features in each model.Firstly, we observe that the DNNs cluster the majority of cells from the same class together, which shows their underlying discriminative power.
HCPL narrows the performance gap between AI methods and human experts and provides a toolbox of methods to tackle the challenges of single-cell protein localisation successfully. This will help accelerate the characterisation of unknown proteins and our understanding of cellular function and biology to advance our knowledge of disease-related phenotypes and drug discovery.Our work uses the HPA dataset provided by the Human Protein Atlas - Single Cell Classification Kaggle challenge.
. The mean value was calculated over the 19 segmentable classes of the challenge with a mask-to-mask IoU > 0.6 as described below:
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Engineered bacterial swarm patterns as spatial records of environmental inputs - Nature Chemical BiologyThe bacterium Proteus mirabilis natively forms a bullseye colony pattern by swarming. Doshi et al. engineered this bacterium to encode environmental inputs, including copper, into its pattern features, and decoded them with image processing and deep learning.
Engineered bacterial swarm patterns as spatial records of environmental inputs - Nature Chemical BiologyThe bacterium Proteus mirabilis natively forms a bullseye colony pattern by swarming. Doshi et al. engineered this bacterium to encode environmental inputs, including copper, into its pattern features, and decoded them with image processing and deep learning.
Weiterlesen »
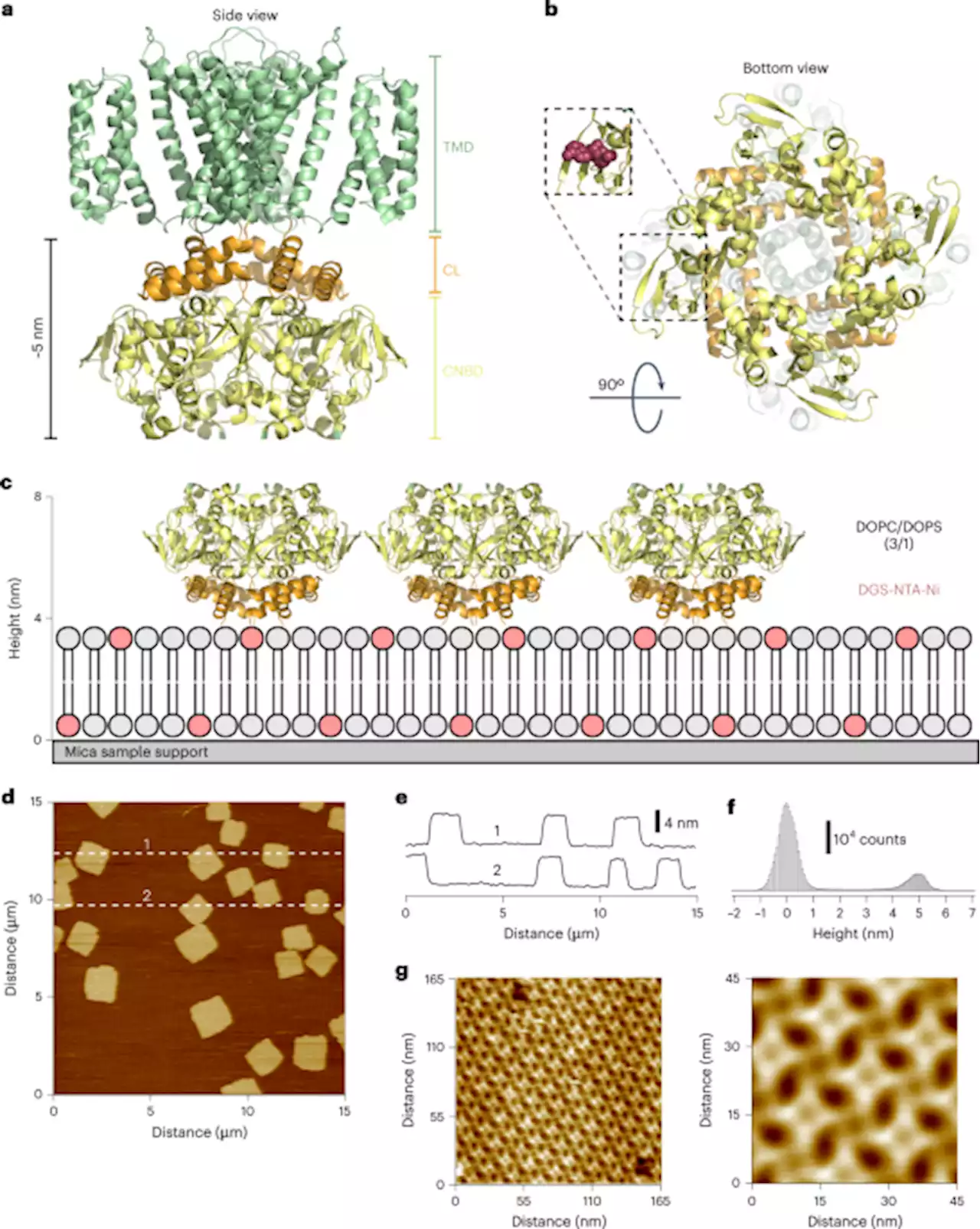 Discrimination between cyclic nucleotides in a cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel - Nature Structural & Molecular BiologyUsing atomic force microscopy, Pan et al. show that cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel SthK, which can be differentially activated by cAMP and cGMP, binds both cyclic nucleotides but only cAMP can access a deep-bound state that could be essential for cAMP-dependent channel activation.
Discrimination between cyclic nucleotides in a cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel - Nature Structural & Molecular BiologyUsing atomic force microscopy, Pan et al. show that cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel SthK, which can be differentially activated by cAMP and cGMP, binds both cyclic nucleotides but only cAMP can access a deep-bound state that could be essential for cAMP-dependent channel activation.
Weiterlesen »
 Long-range skin Josephson supercurrent across a van der Waals ferromagnet - Nature CommunicationsWhen entering a ferromagnet, a spin-singlet supercurrent decays rapidly, while a spin-triplet supercurrent can extend over much longer distances. Here, the authors observe long-range, spin triplet supercurrent in lateral Josephson junctions constructed using the van der Waals metallic ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2 as the weak link.
Long-range skin Josephson supercurrent across a van der Waals ferromagnet - Nature CommunicationsWhen entering a ferromagnet, a spin-singlet supercurrent decays rapidly, while a spin-triplet supercurrent can extend over much longer distances. Here, the authors observe long-range, spin triplet supercurrent in lateral Josephson junctions constructed using the van der Waals metallic ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2 as the weak link.
Weiterlesen »
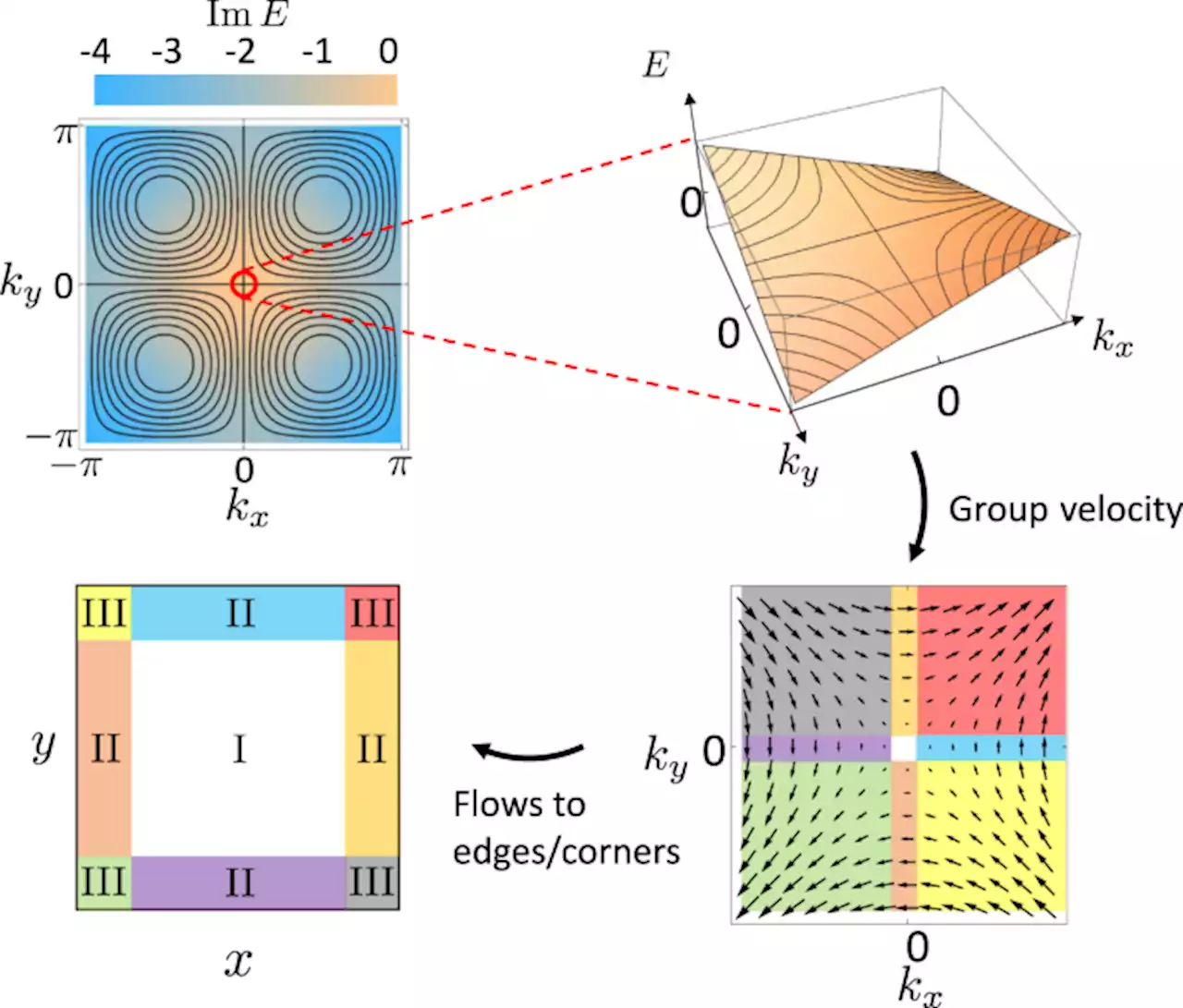 Higher rank chirality and non-Hermitian skin effect in a topolectrical circuit - Nature CommunicationsIn this work, the authors implement a crystalline rank-2 chiral modes by employing non-Hermitian dynamics. They showed the momentum-resolved dynamics and non-Hermitian skin effect associated with the rank-2 chirality both theoretically and experimentally.
Higher rank chirality and non-Hermitian skin effect in a topolectrical circuit - Nature CommunicationsIn this work, the authors implement a crystalline rank-2 chiral modes by employing non-Hermitian dynamics. They showed the momentum-resolved dynamics and non-Hermitian skin effect associated with the rank-2 chirality both theoretically and experimentally.
Weiterlesen »
 Why Communications and Marketing Execs Are Getting CEO JobsFashion’s future CEOs may be very familiar to the media crowd as a growing number of brand-shaping gurus are entering the corner office.
Why Communications and Marketing Execs Are Getting CEO JobsFashion’s future CEOs may be very familiar to the media crowd as a growing number of brand-shaping gurus are entering the corner office.
Weiterlesen »
 China to launch communications relay satellite to the moon in early 2024Queqiao 2 will support a number of upcoming ambitious moon missions.
China to launch communications relay satellite to the moon in early 2024Queqiao 2 will support a number of upcoming ambitious moon missions.
Weiterlesen »