Study reveals new insights into human gut-brainconnection NatureComms
, providing a novel approach to study this intricate connection. The capsule was developed by Vibrant Ltd. Participants in the study included healthy adult male and female volunteers ages 18-40.
, indicating potential for studying this method in different clinical populations. This is a significant breakthrough as it demonstrates the feasibility of this novel approach to studying gut feelings.in certain areas of the brain specifically induced by capsule stimulation. These neural responses increased in amplitude depending on the intensity of the stimulation and were significantly correlated with perceptual accuracy.
"The potential clinical implications for the results of this study are substantial," said Dr. Khalsa."The vibrating capsule method could transform the clinical approach to disorders of gut-brain interaction, including eating disorders and certain gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome or functional dyspepsia."
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Obesity impairs the brain's response to nutrients, suggests studyBrain responses to specific nutrients are diminished in individuals with obesity and are not improved after weight loss, according to a study led by Amsterdam UMC and Yale University, published today in Nature Metabolism.
Obesity impairs the brain's response to nutrients, suggests studyBrain responses to specific nutrients are diminished in individuals with obesity and are not improved after weight loss, according to a study led by Amsterdam UMC and Yale University, published today in Nature Metabolism.
Weiterlesen »
 Spaceflight experience alters human brain structure, posing challenges for long-term missionsSpaceflight impacts brain structure. Longer missions lead to greater ventricle expansion, especially within the first 6 months. Shorter inter-mission intervals limit ventricle recovery. Findings reveal limits and recovery capacity of the brain during spaceflight.
Spaceflight experience alters human brain structure, posing challenges for long-term missionsSpaceflight impacts brain structure. Longer missions lead to greater ventricle expansion, especially within the first 6 months. Shorter inter-mission intervals limit ventricle recovery. Findings reveal limits and recovery capacity of the brain during spaceflight.
Weiterlesen »
 Research brings hope for early treatment of brain degeneration in children with xeroderma pigmentosumXeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a rare and devastating genetic disorder characterized by an inability to repair skin damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) light. As a result, patients with XP develop skin cancers, usually in childhood. Once diagnosed, they can be protected by avoiding sunlight (hence sometimes being called 'children of the night'), wearing special clothing and sunglasses, and using sunscreen.
Research brings hope for early treatment of brain degeneration in children with xeroderma pigmentosumXeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a rare and devastating genetic disorder characterized by an inability to repair skin damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) light. As a result, patients with XP develop skin cancers, usually in childhood. Once diagnosed, they can be protected by avoiding sunlight (hence sometimes being called 'children of the night'), wearing special clothing and sunglasses, and using sunscreen.
Weiterlesen »
 Revolution in neuroscience: 2D nanomaterials propel advances in brain repair, treatment, and diagnosisReview discusses the increasing importance of two-dimensional nanomaterials like graphene in neuroscience, highlighting their potential in nerve repair, creating brain-mimicking synaptic devices, and treating neurological disorders. It also considers the challenges and future prospects of these materials in this complex field.
Revolution in neuroscience: 2D nanomaterials propel advances in brain repair, treatment, and diagnosisReview discusses the increasing importance of two-dimensional nanomaterials like graphene in neuroscience, highlighting their potential in nerve repair, creating brain-mimicking synaptic devices, and treating neurological disorders. It also considers the challenges and future prospects of these materials in this complex field.
Weiterlesen »
 The brain needs 3 years to recover between trips to spaceSpace isn't something we can just get used to, suggesting a rethink of mission durations and frequency
The brain needs 3 years to recover between trips to spaceSpace isn't something we can just get used to, suggesting a rethink of mission durations and frequency
Weiterlesen »
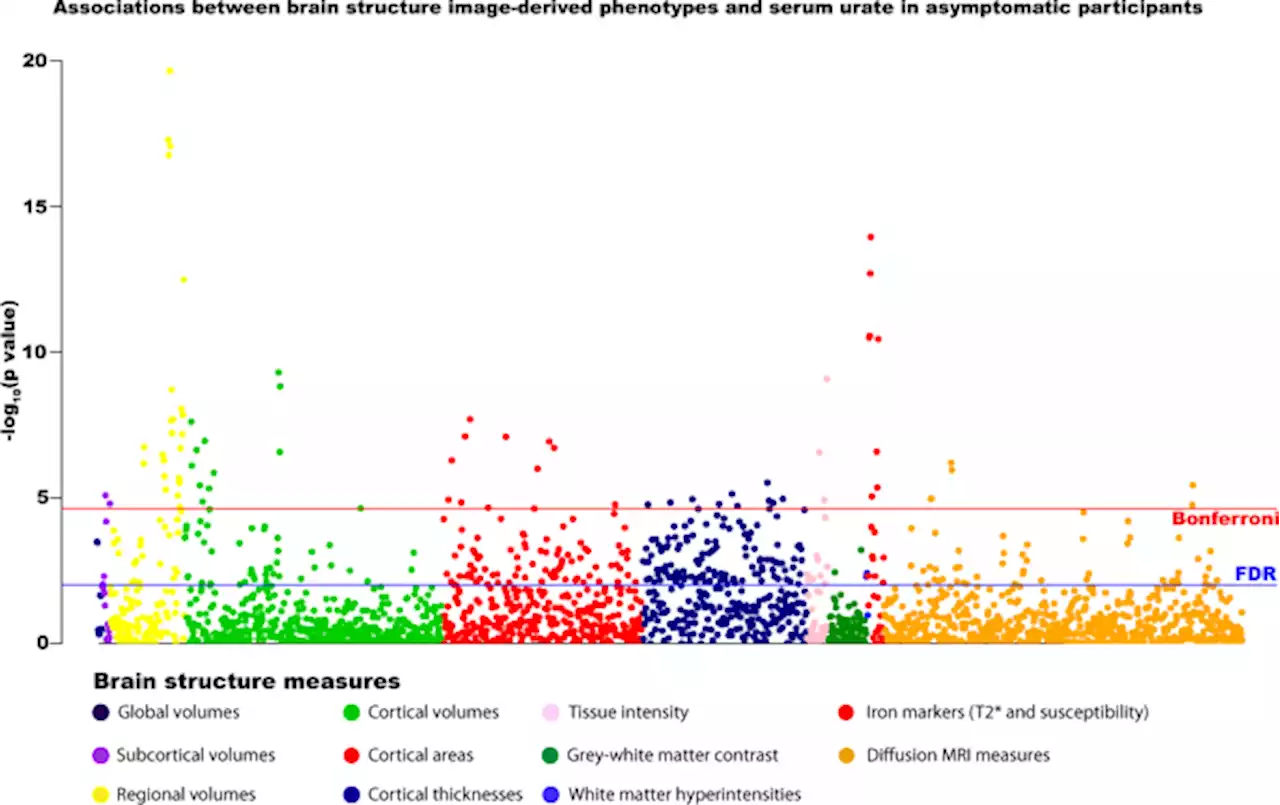 Association of gout with brain reserve and vulnerability to neurodegenerative disease - Nature CommunicationsThe potential association between neurodegenerative disease risk and gout is not fully understood. Here the authors showed that gout is causally related to several measures of brain structure which may explain their higher vulnerability to dementia.
Association of gout with brain reserve and vulnerability to neurodegenerative disease - Nature CommunicationsThe potential association between neurodegenerative disease risk and gout is not fully understood. Here the authors showed that gout is causally related to several measures of brain structure which may explain their higher vulnerability to dementia.
Weiterlesen »