Researchers found that adherence and persistence in T2D patients using oral semaglutide is similar to DPP-4i, but semaglutide users required fewer concurrent medications, indicating higher long-term efficacy.
By Hugo Francisco de SouzaReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.Jul 16 2024 In a recent large-scale retrospective cohort study published in the journal Primary Care Diabetes, researchers used a comprehensive database-derived dataset to evaluate the adherence and persistence of newly initiating oral semaglutide type 2 diabetes patients compared to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor users.
Background Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels as a result of the body's inability to produce or utilize insulin properly. The International Diabetes Federation estimates that 11.3% of all adults have diabetes , with more than 90% of these patients having T2D. In the United States alone, more than 95% of its 37 million diabetic patients report T2D, with projections expecting this prevalence to only increase in the coming decades.
About the study The present study evaluated US-based T2D patient adherence and persistence to semaglutide by comparing their patterns to those of DPP-4i. The study was a non-interventional, retrospective, cohort-based study using data from two administrative healthcare databases – the Merative MarketScan Commercial and the Medicare databases. These databases contain data across age groups and from all 50 US states.
Study findings After excluding participants with missing data, the final dataset comprised 5,485 and 4,980 T2D patients prescribed semaglutide and DPP-4i, respectively. Ps-IPW analyses revealed that demographic characteristics between both cohorts were statistically comparable, with 'out-of-pocket costs' and obesity being the only exception. Semaglutide costs amounted to an average of $103 compared to the DPP-4i average of $67 per 30 days.
Semaglutide Type 2 Diabetes Blood Blood Sugar Chronic Efficacy GLP-1 High Blood Sugar Insulin Primary Care
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 New study sheds light on potassium channels to help researchers design better drugsPotassium channels are openings that allow charged potassium atoms to cross the cell membrane. Voltage-gated potassium channels—which open only when a specific voltage is reached across the cell membrane—are essential for the electrical impulses that nerve cells or neurons use to communicate.
New study sheds light on potassium channels to help researchers design better drugsPotassium channels are openings that allow charged potassium atoms to cross the cell membrane. Voltage-gated potassium channels—which open only when a specific voltage is reached across the cell membrane—are essential for the electrical impulses that nerve cells or neurons use to communicate.
Weiterlesen »
 Q&A: Researchers discuss study showing maternal cell phone use may negatively impact infant language developmentResearch suggests that phone use may have an effect on children's speech input and language development. However, most of the prior work in this area examines parents and children in controlled laboratory experiments in public spaces and may not be representative of daily interactions between a child and their caregivers.
Q&A: Researchers discuss study showing maternal cell phone use may negatively impact infant language developmentResearch suggests that phone use may have an effect on children's speech input and language development. However, most of the prior work in this area examines parents and children in controlled laboratory experiments in public spaces and may not be representative of daily interactions between a child and their caregivers.
Weiterlesen »
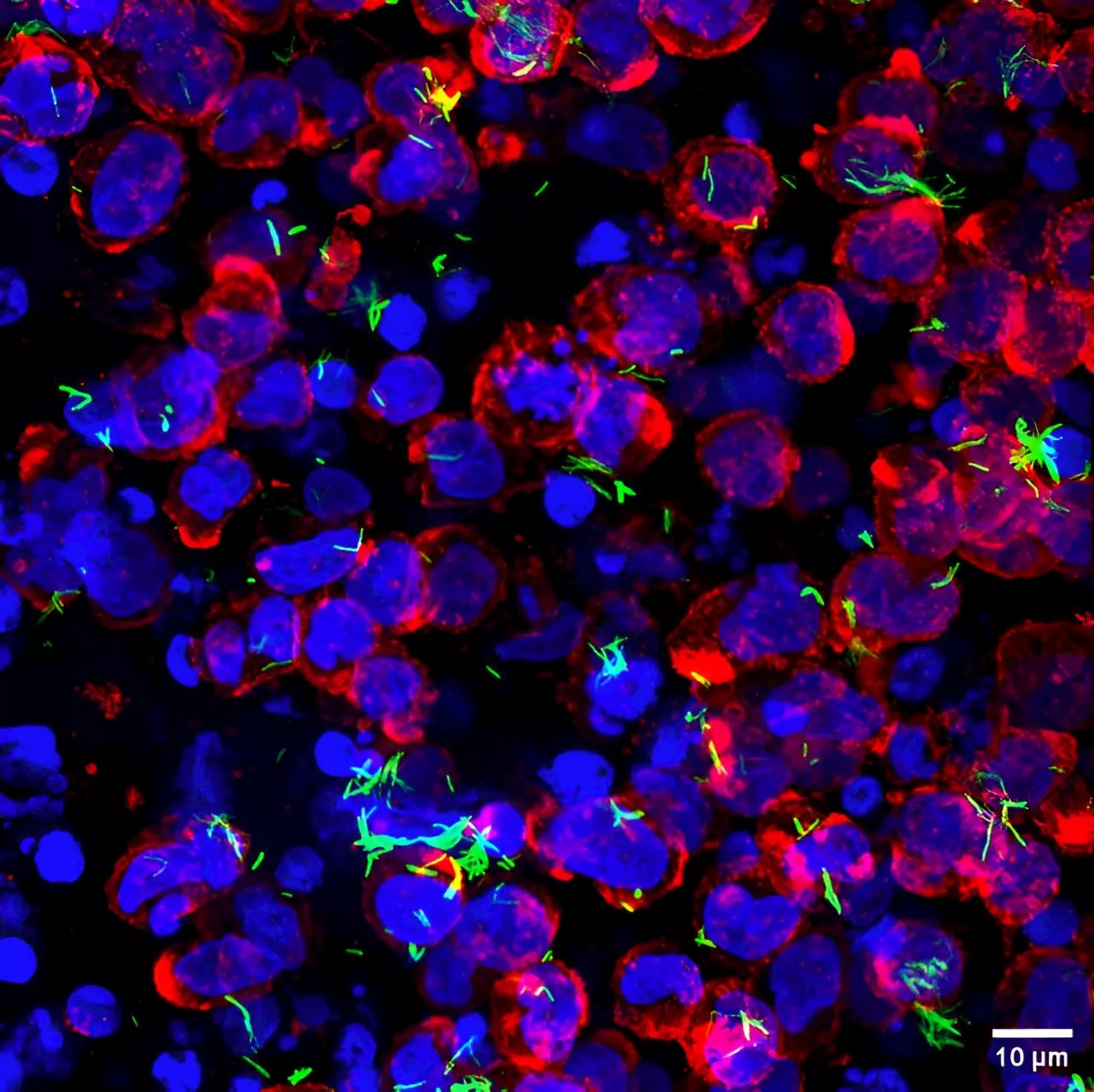 Researchers design novel 3D hydrogel culture to study TB infection and treatmentResearchers from the Department of Bioengineering (BE), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), have designed a novel 3D hydrogel culture system that mimics the mammalian lung environment. It provides a powerful platform to track and study how tuberculosis bacteria infect lung cells and test the efficacy of therapeutics used to treat TB.
Researchers design novel 3D hydrogel culture to study TB infection and treatmentResearchers from the Department of Bioengineering (BE), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), have designed a novel 3D hydrogel culture system that mimics the mammalian lung environment. It provides a powerful platform to track and study how tuberculosis bacteria infect lung cells and test the efficacy of therapeutics used to treat TB.
Weiterlesen »
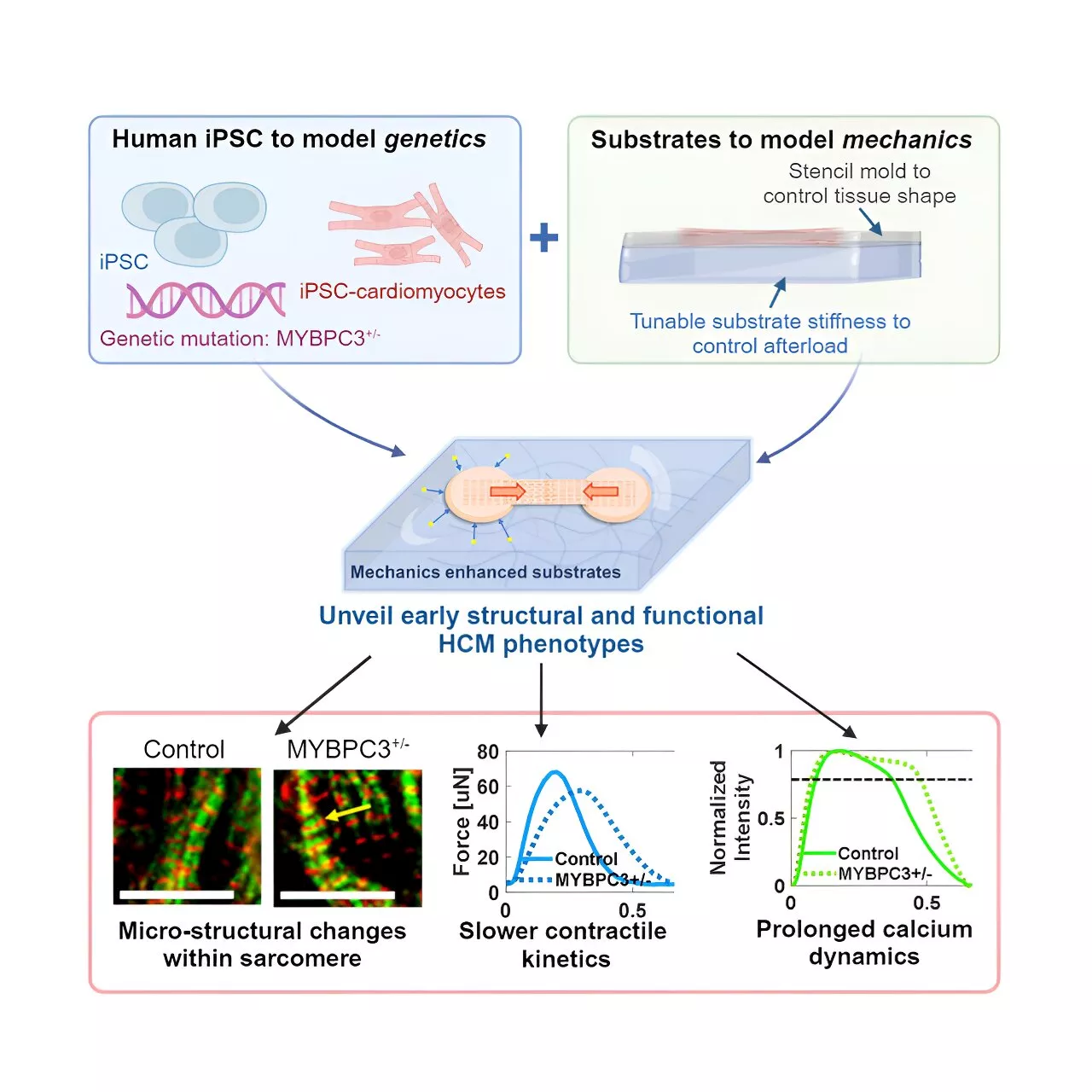 Researchers more effectively study mutations that cause heart disease by putting cells through their pacesUsing animals to study heart disease doesn't always translate well to human health outcomes, and human heart cells available for research don't work outside the human body.
Researchers more effectively study mutations that cause heart disease by putting cells through their pacesUsing animals to study heart disease doesn't always translate well to human health outcomes, and human heart cells available for research don't work outside the human body.
Weiterlesen »
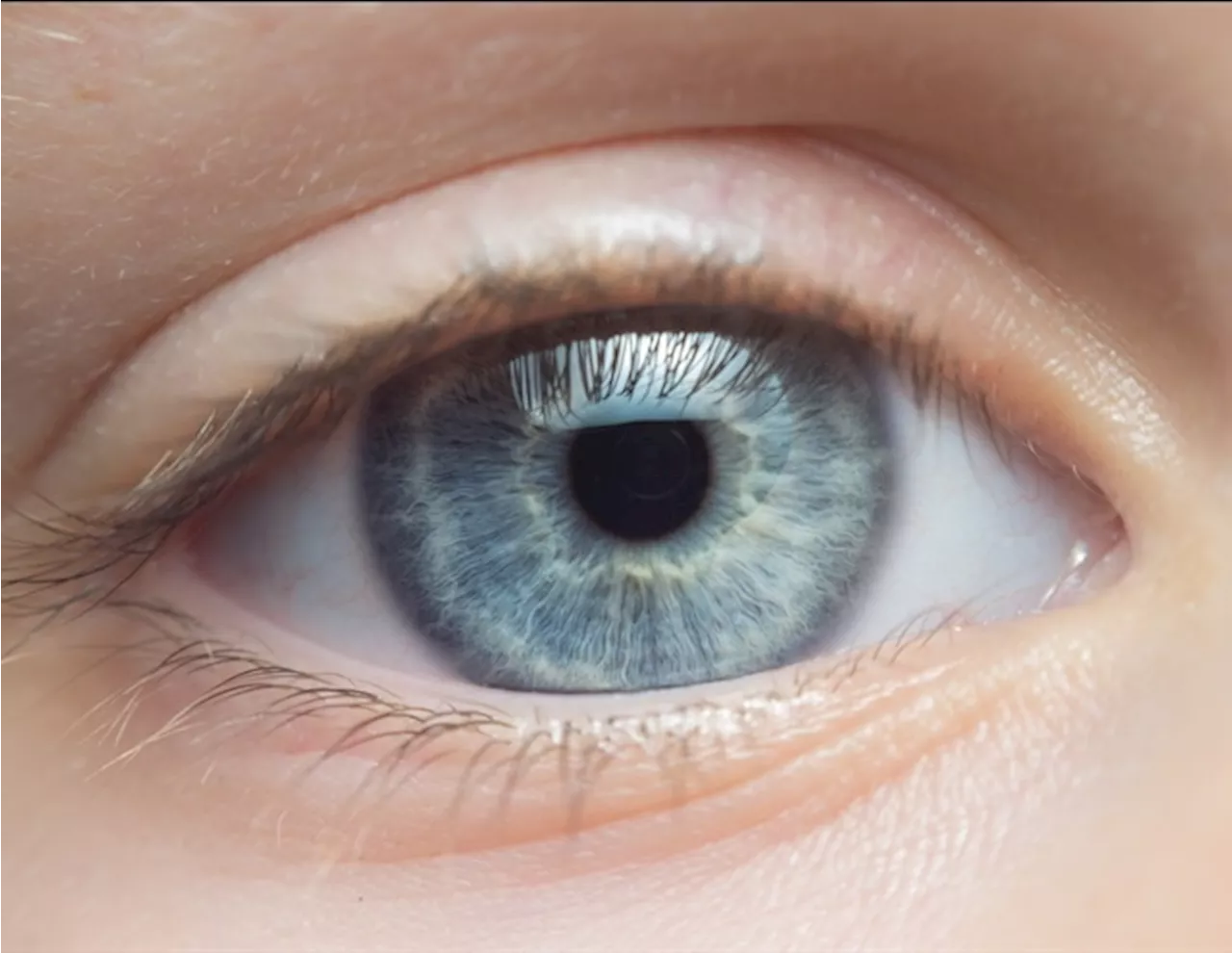 Texas A&M researchers study impact of space travel on eye healthAs space travel becomes more common, it is important to consider the impacts of space flight and altered gravity on the human body. Led by Dr. Ana Diaz Artiles, researchers at Texas A&M University are studying some of those impacts, specifically effects on the eye.
Texas A&M researchers study impact of space travel on eye healthAs space travel becomes more common, it is important to consider the impacts of space flight and altered gravity on the human body. Led by Dr. Ana Diaz Artiles, researchers at Texas A&M University are studying some of those impacts, specifically effects on the eye.
Weiterlesen »
 Researchers study differences in attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccines between women and men in AfricaWhile many studies over the past several years have examined people's access to and attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccines, few studies in sub-Saharan Africa have looked at whether there were differences in vaccination rates and intention between men and women.
Researchers study differences in attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccines between women and men in AfricaWhile many studies over the past several years have examined people's access to and attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccines, few studies in sub-Saharan Africa have looked at whether there were differences in vaccination rates and intention between men and women.
Weiterlesen »
