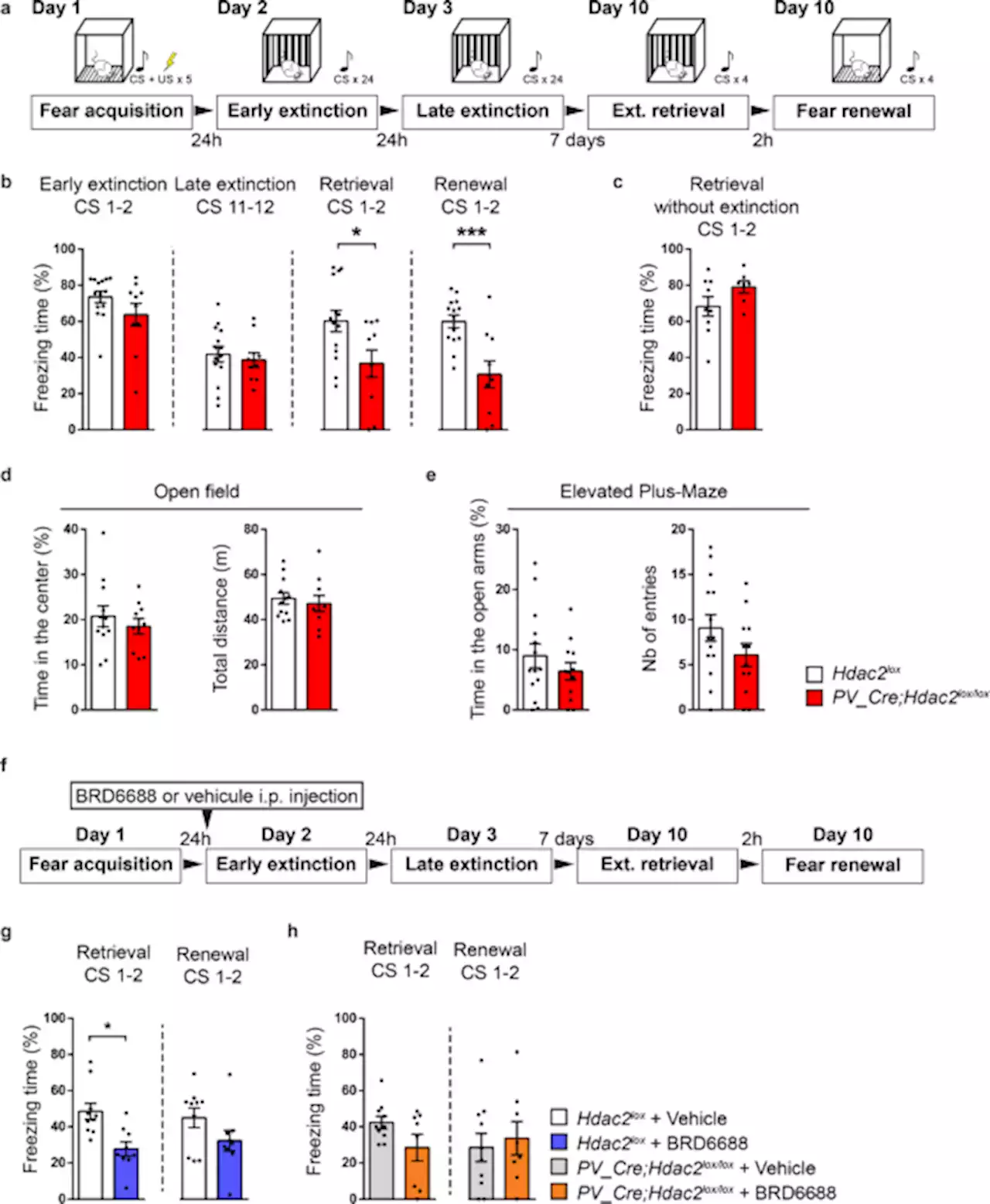
Mimicking brainplasticity in children to control post-traumatic stress MolPsychiatry
, 32037). All animals were maintained under a light-dark cycle in a temperature and humidity-controlled room. Food and water were available. All procedures described here had been approved by the Comité Institutionnel de Bonnes Pratiques Animales en Recherche of the Research Center of Sainte-Justine Hospital in accordance with the principles published in the Canadian Council on Animal’s Care’s .
The primary antibodies used in this study and their working concentrations are as follows: rabbit monoclonal anti-Hdac2 ; mouse monoclonal anti-PV ; rabbit polyclonal anti-PV ; guinea pig polyclonal anti-PV ; mouse monoclonal anti-gephyrin ; rabbit polyclonal anti-aggrecan ; chicken polyclonal anti-GFP . To label PNNs, a solution of biotin-conjugated lectin Wisteria floribunda was added in the primary antibody solution.
The secondary antibodies used in this study and their working concentrations are as follows: goat anti-chicken Alexa488 conjugated , goat anti-rabbit Alexa633 conjugated , goat anti-mouse Alexa555 conjugated , goat anti-mouse Alexa647 conjugated , goat anti-rabbit Alexa555 conjugated , goat anti-guinea pig Alexa647 conjugated and Alexa 568-conjugated streptavidin .
All immunohistological experiments were performed on at least three different sections per brain region per animal. No mice were excluded from the following analysis.All images were acquired using Leica confocal microscopes . We imaged somatosensory and prefrontal cortex layer 5 and basolateral amygdala using 20X multi-immersion and 63X oil objectives. We focussed on layer 5 of SSCX and PFC because PVcells are more abundant in this layer.
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 The association between gut microbiota and postoperative delirium in patients - Translational PsychiatryTranslational Psychiatry - The association between gut microbiota and postoperative delirium in patients
The association between gut microbiota and postoperative delirium in patients - Translational PsychiatryTranslational Psychiatry - The association between gut microbiota and postoperative delirium in patients
Weiterlesen »
 Molecular trigger for breast cancer development identifiedIn what may turn out to be a long-missing piece in the puzzle of breast cancer, Harvard Medical School researchers have identified the molecular sparkplug that ignites cases of the disease currently unexplained by the classical model of breast-cancer development. A report on the team's work is published May 17 in Nature.
Molecular trigger for breast cancer development identifiedIn what may turn out to be a long-missing piece in the puzzle of breast cancer, Harvard Medical School researchers have identified the molecular sparkplug that ignites cases of the disease currently unexplained by the classical model of breast-cancer development. A report on the team's work is published May 17 in Nature.
Weiterlesen »
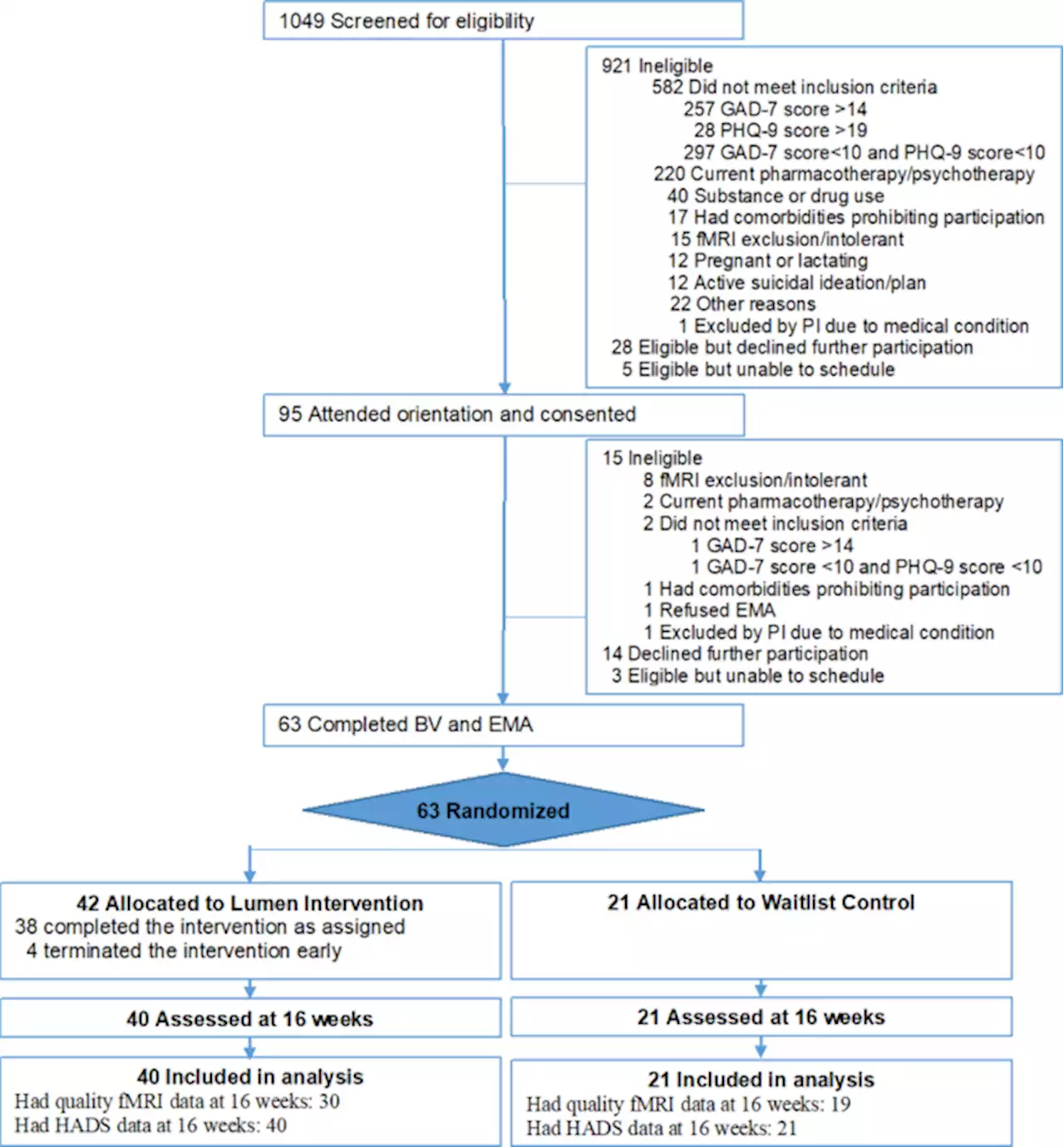 Effects of a virtual voice-based coach delivering problem-solving treatment on emotional distress and brain function: a pilot RCT in depression and anxiety - Translational PsychiatryTranslational Psychiatry - Effects of a virtual voice-based coach delivering problem-solving treatment on emotional distress and brain function: a pilot RCT in depression and anxiety
Effects of a virtual voice-based coach delivering problem-solving treatment on emotional distress and brain function: a pilot RCT in depression and anxiety - Translational PsychiatryTranslational Psychiatry - Effects of a virtual voice-based coach delivering problem-solving treatment on emotional distress and brain function: a pilot RCT in depression and anxiety
Weiterlesen »
 Co-infection of dengue and Zika viruses mutually enhances viral replication in the mosquito Aedes aegypti - Parasites & VectorsBackground The mosquito Aedes aegypti transmits two of the most serious mosquito-borne viruses, dengue virus (DENV) and Zika virus (ZIKV), which results in significant human morbidity and mortality worldwide. The quickly shifting landscapes of DENV and ZIKV endemicity worldwide raise concerns that their co-circulation through the Ae. aegypti mosquito vector could greatly exacerbate the disease burden in humans. Recent reports have indicated an increase in the number of co-infection cases in expanding co-endemic regions; however, the impact of co-infection on viral infection and the detailed molecular mechanisms remain to be defined. Methods C6/36 (Aedes albopictus) cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium/Mitsuhashi and Maramorosch Insect Medium (DMEM/MM) (1:1) containing 2% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum and 1× penicillin/streptomycin solution. For virus propagation, the cells were infected with either DENV serotype 2 (DENV2) strain 16681 or ZIKV isolate Thailand/1610acTw (MF692778.1). Mosquitoes (Ae. aegypti UGAL [University of Georgia Laboratory]/Rockefeller strain) were orally infected with DENV2 and ZIKV through infectious blood-feeding. Results We first examined viral replication activity in cells infected simultaneously, or sequentially, with DENV and ZIKV, and found interspecies binding of viral genomic transcripts to the non-structural protein 5 (NS5). When we challenged Ae. aegypti mosquitos with both DENV2 and ZIKV sequentially to probe similar interactions, virus production and vector susceptibility to infection were significantly enhanced. Conclusions Our results suggest that DENV2 and ZIKV simultaneously establishing infection in the Ae. aegypti mosquito vector may augment one another during replication. The data also implicate the homologous NS5 protein as a key intersection between the flaviviruses in co-infection, highlighting it as a potential target for vector control.
Co-infection of dengue and Zika viruses mutually enhances viral replication in the mosquito Aedes aegypti - Parasites & VectorsBackground The mosquito Aedes aegypti transmits two of the most serious mosquito-borne viruses, dengue virus (DENV) and Zika virus (ZIKV), which results in significant human morbidity and mortality worldwide. The quickly shifting landscapes of DENV and ZIKV endemicity worldwide raise concerns that their co-circulation through the Ae. aegypti mosquito vector could greatly exacerbate the disease burden in humans. Recent reports have indicated an increase in the number of co-infection cases in expanding co-endemic regions; however, the impact of co-infection on viral infection and the detailed molecular mechanisms remain to be defined. Methods C6/36 (Aedes albopictus) cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium/Mitsuhashi and Maramorosch Insect Medium (DMEM/MM) (1:1) containing 2% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum and 1× penicillin/streptomycin solution. For virus propagation, the cells were infected with either DENV serotype 2 (DENV2) strain 16681 or ZIKV isolate Thailand/1610acTw (MF692778.1). Mosquitoes (Ae. aegypti UGAL [University of Georgia Laboratory]/Rockefeller strain) were orally infected with DENV2 and ZIKV through infectious blood-feeding. Results We first examined viral replication activity in cells infected simultaneously, or sequentially, with DENV and ZIKV, and found interspecies binding of viral genomic transcripts to the non-structural protein 5 (NS5). When we challenged Ae. aegypti mosquitos with both DENV2 and ZIKV sequentially to probe similar interactions, virus production and vector susceptibility to infection were significantly enhanced. Conclusions Our results suggest that DENV2 and ZIKV simultaneously establishing infection in the Ae. aegypti mosquito vector may augment one another during replication. The data also implicate the homologous NS5 protein as a key intersection between the flaviviruses in co-infection, highlighting it as a potential target for vector control.
Weiterlesen »
 Sex differences in the polygenic architecture of hearing problems in adults - Genome MedicineBackground Hearing problems (HP) in adults are common and are associated with several comorbid conditions. Its prevalence increases with age, reflecting the cumulative effect of environmental factors and genetic predisposition. Although several risk loci have been already identified, HP biology and epidemiology are still insufficiently investigated by large-scale genetic studies. Methods Leveraging the UK Biobank, the Nurses’ Health Studies (I and II), the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, and the Million Veteran Program, we conducted a comprehensive genome-wide investigation of HP in 748,668 adult participants (discovery N = 501,825; replication N = 226,043; cross-ancestry replication N = 20,800). We leveraged the GWAS findings to characterize HP polygenic architecture, exploring sex differences, polygenic risk across ancestries, tissue-specific transcriptomic regulation, cause-effect relationships with genetically correlated traits, and gene interactions with HP environmental risk factors. Results We identified 54 risk loci and demonstrated that HP polygenic risk is shared across ancestry groups. Our transcriptomic regulation analysis highlighted the potential role of the central nervous system in HP pathogenesis. The sex-stratified analyses showed several additional associations related to peripheral hormonally regulated tissues reflecting a potential role of estrogen in hearing function. This evidence was supported by the multivariate interaction analysis that showed how genes involved in brain development interact with sex, noise pollution, and tobacco smoking in relation to their HP associations. Additionally, the genetically informed causal inference analysis showed that HP is linked to many physical and mental health outcomes. Conclusions The results provide many novel insights into the biology and epidemiology of HP in adults. Our sex-specific analyses and transcriptomic associations highlighted molecular pathways that may be targeted for drug developme
Sex differences in the polygenic architecture of hearing problems in adults - Genome MedicineBackground Hearing problems (HP) in adults are common and are associated with several comorbid conditions. Its prevalence increases with age, reflecting the cumulative effect of environmental factors and genetic predisposition. Although several risk loci have been already identified, HP biology and epidemiology are still insufficiently investigated by large-scale genetic studies. Methods Leveraging the UK Biobank, the Nurses’ Health Studies (I and II), the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, and the Million Veteran Program, we conducted a comprehensive genome-wide investigation of HP in 748,668 adult participants (discovery N = 501,825; replication N = 226,043; cross-ancestry replication N = 20,800). We leveraged the GWAS findings to characterize HP polygenic architecture, exploring sex differences, polygenic risk across ancestries, tissue-specific transcriptomic regulation, cause-effect relationships with genetically correlated traits, and gene interactions with HP environmental risk factors. Results We identified 54 risk loci and demonstrated that HP polygenic risk is shared across ancestry groups. Our transcriptomic regulation analysis highlighted the potential role of the central nervous system in HP pathogenesis. The sex-stratified analyses showed several additional associations related to peripheral hormonally regulated tissues reflecting a potential role of estrogen in hearing function. This evidence was supported by the multivariate interaction analysis that showed how genes involved in brain development interact with sex, noise pollution, and tobacco smoking in relation to their HP associations. Additionally, the genetically informed causal inference analysis showed that HP is linked to many physical and mental health outcomes. Conclusions The results provide many novel insights into the biology and epidemiology of HP in adults. Our sex-specific analyses and transcriptomic associations highlighted molecular pathways that may be targeted for drug developme
Weiterlesen »
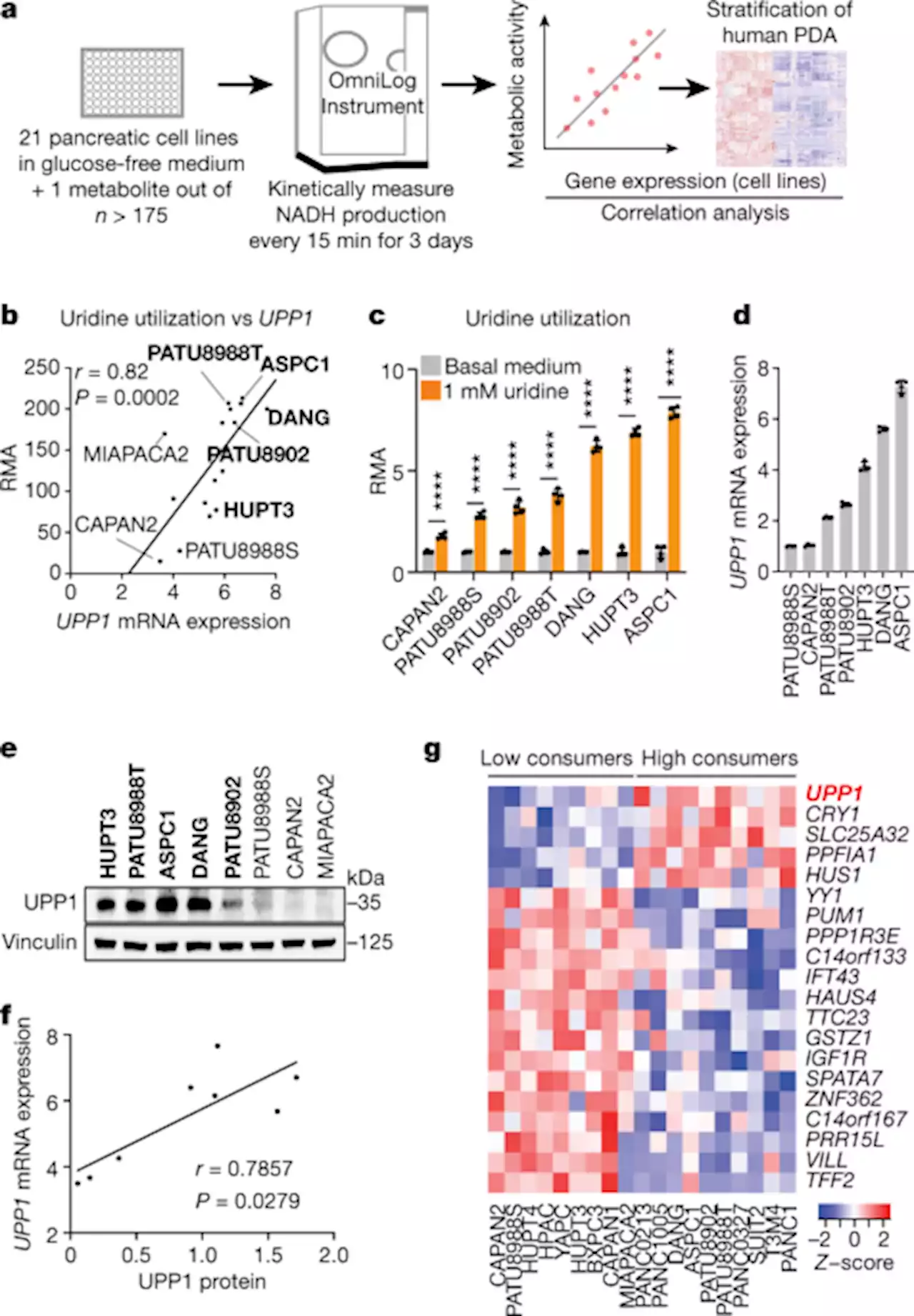 Uridine-derived ribose fuels glucose-restricted pancreatic cancer - NatureA metabolite screen of pancreatic cells shows that pancreatic cancer cells metabolize uridine-derived ribose via UPP1, supporting redox balance, survival and proliferation.
Uridine-derived ribose fuels glucose-restricted pancreatic cancer - NatureA metabolite screen of pancreatic cells shows that pancreatic cancer cells metabolize uridine-derived ribose via UPP1, supporting redox balance, survival and proliferation.
Weiterlesen »