Eating any amount of fish during pregnancy was associated with about a 20% lower likelihood of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis, particularly in females, and a slight reduction in autism-related traits in offspring, according to a new study funded by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program at the National...
Environmental influences on Child Health OutcomesSep 3 2024 Eating any amount of fish during pregnancy was associated with about a 20% lower likelihood of autism spectrum disorder diagnosis, particularly in females, and a slight reduction in autism-related traits in offspring, according to a new study funded by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes Program at the National Institutes of Health.
ECHO Cohort researchers wanted to see whether low fish consumption and omega-3 supplement use during pregnancy might be associated with the occurrence of an autism diagnosis or parent-reported autism-related traits. What happened during the study? Researchers analyzed data from about 4,000 participants, examining the relationships among fish intake, supplement use, and neurodevelopmental outcomes related to autism.
Consuming fish during pregnancy was associated with a lower likelihood of offspring being diagnosed with autism and a slight decrease in total SRS scores compared to not eating fish. These results were consistent across all levels of fish consumption, from "any" amount or "less than once per week" to "more than twice per week." No significant associations were found between omega-3 fish oil supplements and autism diagnosis compared to no use.
Fish Pregnancy Supplements Child Health Fatty Acids Fish Oil Maternal Health Medical Research Nutrition Prenatal Research
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
 Research shows parents' eating habits directly influence children's eating behaviorYoung children often display similar eating behavior as their parents, with a parent's own eating style influencing how they feed their children, research at Aston University has shown.
Research shows parents' eating habits directly influence children's eating behaviorYoung children often display similar eating behavior as their parents, with a parent's own eating style influencing how they feed their children, research at Aston University has shown.
Weiterlesen »
 Catching up on sleep on weekends may lower heart disease risk by up to 20%The demands of the working week, often influenced by school or work schedules, can lead to sleep disruption and deprivation. However, new research presented at ESC Congress 2024 shows that people that 'catch up' on their sleep by sleeping in at weekends may see their risk of heart disease fall by one-fifth.
Catching up on sleep on weekends may lower heart disease risk by up to 20%The demands of the working week, often influenced by school or work schedules, can lead to sleep disruption and deprivation. However, new research presented at ESC Congress 2024 shows that people that 'catch up' on their sleep by sleeping in at weekends may see their risk of heart disease fall by one-fifth.
Weiterlesen »
 Weekend sleep could lower heart disease risk by 20%The demands of the working week, often influenced by school or work schedules, can lead to sleep disruption and deprivation.
Weekend sleep could lower heart disease risk by 20%The demands of the working week, often influenced by school or work schedules, can lead to sleep disruption and deprivation.
Weiterlesen »
 Totnes swim site pollution at 20 times acceptable levelVery high E. coli levels are recorded at a site in Devon where hundreds of people are due to swim.
Totnes swim site pollution at 20 times acceptable levelVery high E. coli levels are recorded at a site in Devon where hundreds of people are due to swim.
Weiterlesen »
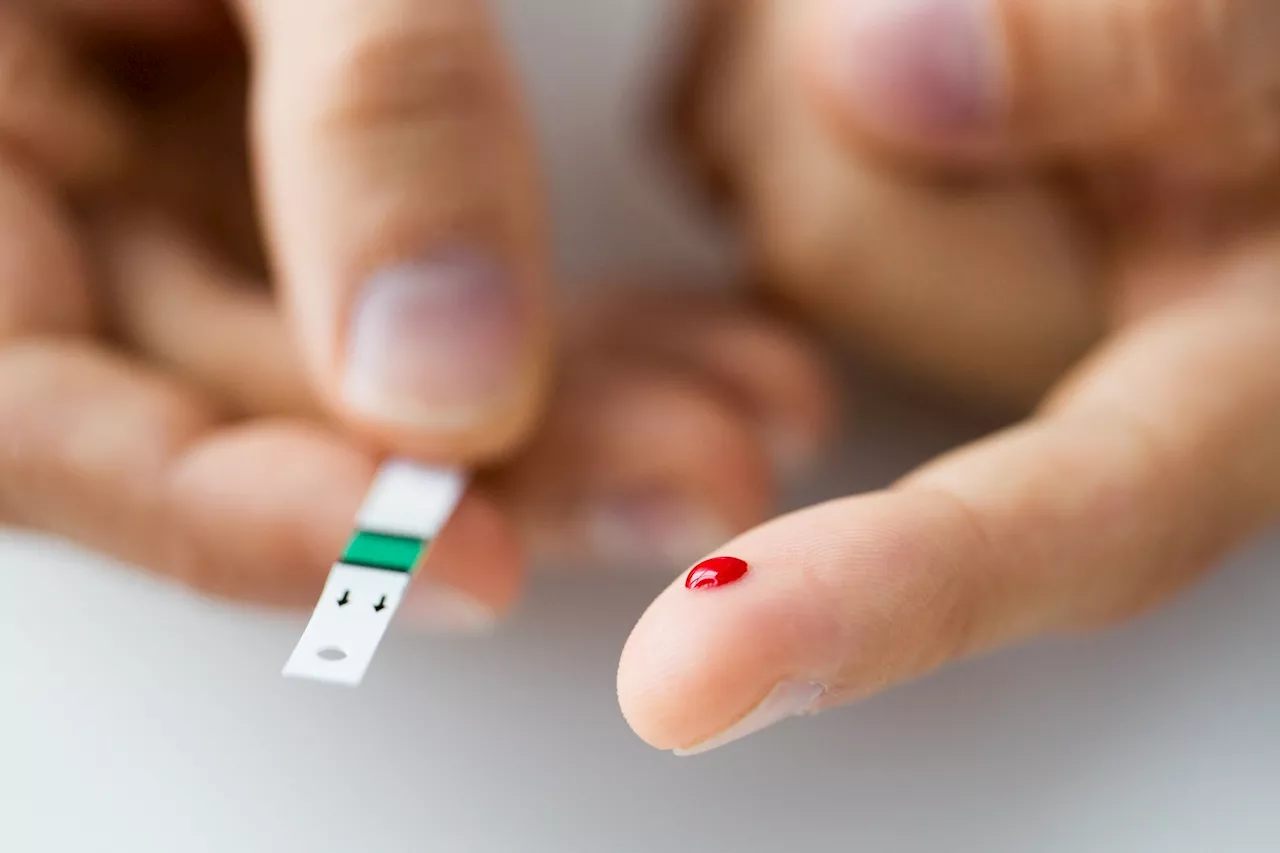 Diabetes accelerates the onset of severe long-term conditions by 15-20 years, cutting life expectancyA study in Nature Medicine reveals that diabetes accelerates the onset of multiple long-term conditions by 15-20 years, significantly reducing life expectancy in English adults.
Diabetes accelerates the onset of severe long-term conditions by 15-20 years, cutting life expectancyA study in Nature Medicine reveals that diabetes accelerates the onset of multiple long-term conditions by 15-20 years, significantly reducing life expectancy in English adults.
Weiterlesen »
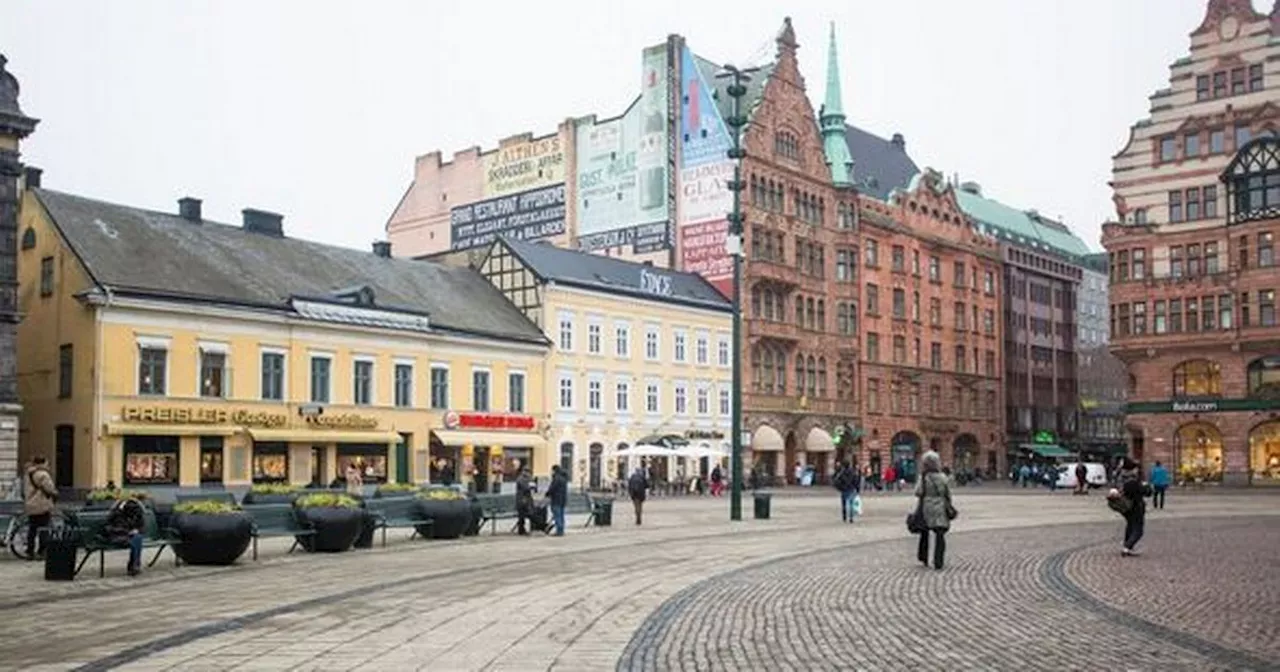 'I visited hidden gem 20 minutes from Copenhagen that isn't full of tourists'Malmo is Sweden's third-largest city and is located just 30 minutes away from Copenhagen in Denmark. Sophie Harris visited the city and found it to be the perfect hidden gem
'I visited hidden gem 20 minutes from Copenhagen that isn't full of tourists'Malmo is Sweden's third-largest city and is located just 30 minutes away from Copenhagen in Denmark. Sophie Harris visited the city and found it to be the perfect hidden gem
Weiterlesen »
