A study published in Gut Pathogens finds that in Indian patients with COVID-19, a dysbiotic gut microbial community may play an important role in disease severity. Modulation of gut microbiota through diet interventions may reduce disease severity.
]. Decarboxylation of histidine to histamine by gut microbes hasalready been reported. This amino acid has potent immunomodulatory effects through activation of histamine receptors and the authors have stated thatProgression of SARS-CoV-2 infection to advanced stages is usuallyaccompanied by a vicious inflammatory response that in the future often leads to multiorgan failure.
Our study has a few limitations, including a relatively small sample size with mild disease, a lack of asymptomatic patients, and a non-COVID control group from the same hospital at the same time, which may have overlooked potential confounding factors. Although a large cohort size would have been desirable to firmly establish a relationship between COVID-19 severity and gut dysbiosis, the taxonomic dysbiosis identified in the present study is significant.
Deutschland Neuesten Nachrichten, Deutschland Schlagzeilen
Similar News:Sie können auch ähnliche Nachrichten wie diese lesen, die wir aus anderen Nachrichtenquellen gesammelt haben.
EU urged to crack down on imports of Indian fuels made with Russian oil\n\t\t\tExpert insights, analysis and smart data help you cut through the noise to spot trends,\n\t\t\trisks and opportunities.\n\t\t\n\t\tJoin over 300,000 Finance professionals who already subscribe to the FT.
Weiterlesen »
 Long Boi: £10k statue plan for missing University of York duckLong Boi, a mallard/Indian runner cross, became famous after featuring on radio and US TV.
Long Boi: £10k statue plan for missing University of York duckLong Boi, a mallard/Indian runner cross, became famous after featuring on radio and US TV.
Weiterlesen »
 Carotenoids' potential in reducing chronic disease riskCarotenoids' potential in reducing chronic disease risk Nutrients_MDPI intestinal microbiota metabolites absorption
Carotenoids' potential in reducing chronic disease riskCarotenoids' potential in reducing chronic disease risk Nutrients_MDPI intestinal microbiota metabolites absorption
Weiterlesen »
 Higher sunlight and vitamin D exposure is associated with a lower likelihood of having high perceived stressHigher sunlight and vitamin D exposure is associated with a lower likelihood of having high perceived stress Nutrients_MDPI vitaminD sunlight exercise stress mentalhealth publichealth mediterraneandiet meddiet MD
Higher sunlight and vitamin D exposure is associated with a lower likelihood of having high perceived stressHigher sunlight and vitamin D exposure is associated with a lower likelihood of having high perceived stress Nutrients_MDPI vitaminD sunlight exercise stress mentalhealth publichealth mediterraneandiet meddiet MD
Weiterlesen »
 Association between adherence to a low carbohydrate dietary (LCD) pattern with breast milk characteristics and oxidative markers in infants’ urine: a cross-sectional study - Journal of Health, Population and NutritionBackground Breast milk (BM) is a dynamic fluid that varies over time and between women. The variations in BM components are most likely associated with maternal diet quality. This study aimed to assess adherence to a low carbohydrate dietary (LCD) pattern with oxidative stress markers of BM characteristics and infants’ urine. Materials and methods In this cross-sectional study 350 breastfeeding mothers and their infants were recruited. BM samples were collected from mothers, and urine specimens were obtained from each infant. To evaluate LCD scores, subjects were divided into 10 deciles according to the percent of energy obtained from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Determination of total antioxidant activity was conducted using the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), 2, 2′-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARs), and Ellman’s assay. Biochemical assays of samples including calcium, total protein, and triglyceride level were also performed using commercial kits. Results Participants with the greatest LCD pattern adherence were placed into the last quartile (Q4), and those with the minimum LCD were in the first quartile (Q1). Individuals in the highest LCD quartile had significantly higher levels of milk FRAP, thiol, and protein, as well as infant urinary FRAP and lower milk MDA levels than those in the lowest quartile. Multivariate linear regression analyses indicated that higher score of the LCD pattern was associated with a higher level of milk thiol, protein, and lower level of milk MDA (p | 0.05). Conclusion Our findings show that adherence to a LCD, as defined by a low level of carbohydrates in daily food intake, is linked with improved BM quality and markers of oxidative stress in infant urine.
Association between adherence to a low carbohydrate dietary (LCD) pattern with breast milk characteristics and oxidative markers in infants’ urine: a cross-sectional study - Journal of Health, Population and NutritionBackground Breast milk (BM) is a dynamic fluid that varies over time and between women. The variations in BM components are most likely associated with maternal diet quality. This study aimed to assess adherence to a low carbohydrate dietary (LCD) pattern with oxidative stress markers of BM characteristics and infants’ urine. Materials and methods In this cross-sectional study 350 breastfeeding mothers and their infants were recruited. BM samples were collected from mothers, and urine specimens were obtained from each infant. To evaluate LCD scores, subjects were divided into 10 deciles according to the percent of energy obtained from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Determination of total antioxidant activity was conducted using the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), 2, 2′-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARs), and Ellman’s assay. Biochemical assays of samples including calcium, total protein, and triglyceride level were also performed using commercial kits. Results Participants with the greatest LCD pattern adherence were placed into the last quartile (Q4), and those with the minimum LCD were in the first quartile (Q1). Individuals in the highest LCD quartile had significantly higher levels of milk FRAP, thiol, and protein, as well as infant urinary FRAP and lower milk MDA levels than those in the lowest quartile. Multivariate linear regression analyses indicated that higher score of the LCD pattern was associated with a higher level of milk thiol, protein, and lower level of milk MDA (p | 0.05). Conclusion Our findings show that adherence to a LCD, as defined by a low level of carbohydrates in daily food intake, is linked with improved BM quality and markers of oxidative stress in infant urine.
Weiterlesen »
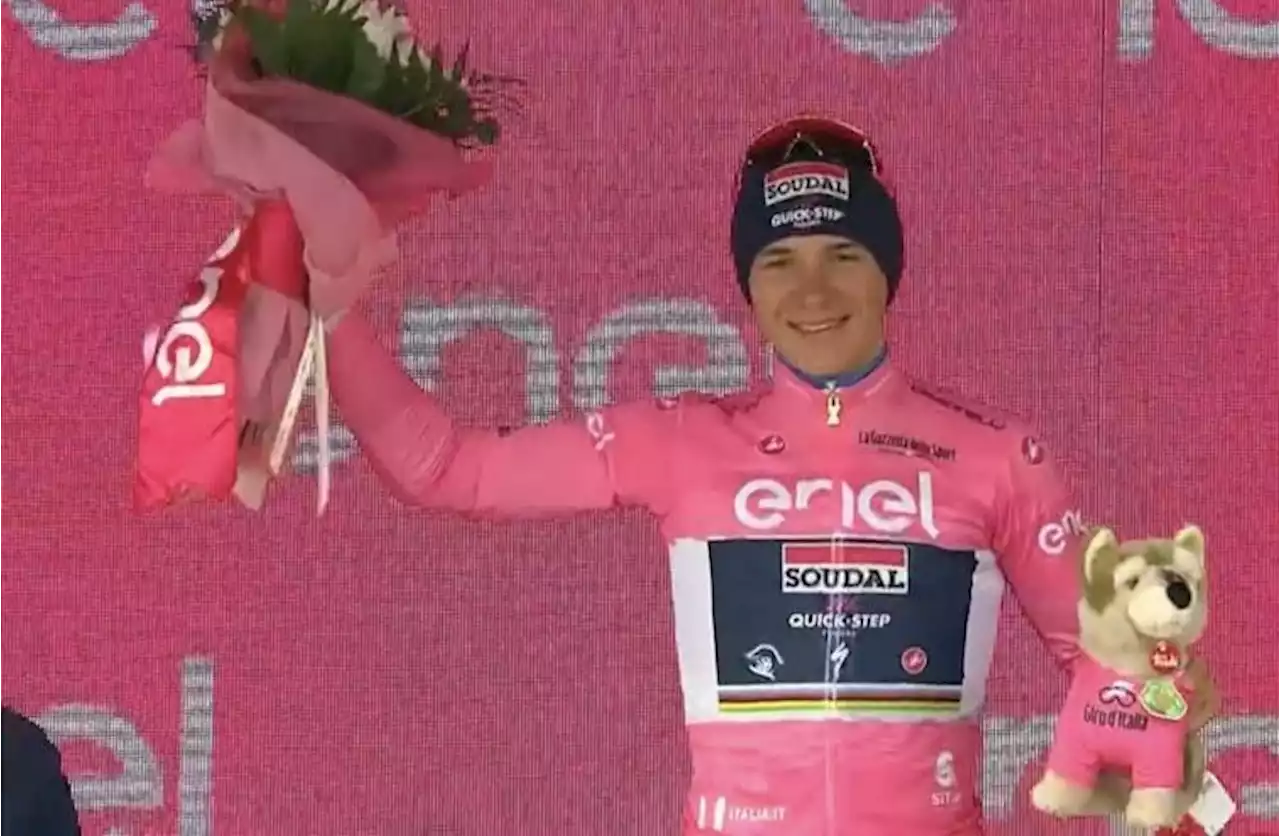 Remco Evenepoel OUT of Giro d'Italia with CovidThe Belgian regained the race lead during yesterday's time trial, but abandoned the race just hours later
Remco Evenepoel OUT of Giro d'Italia with CovidThe Belgian regained the race lead during yesterday's time trial, but abandoned the race just hours later
Weiterlesen »
